| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
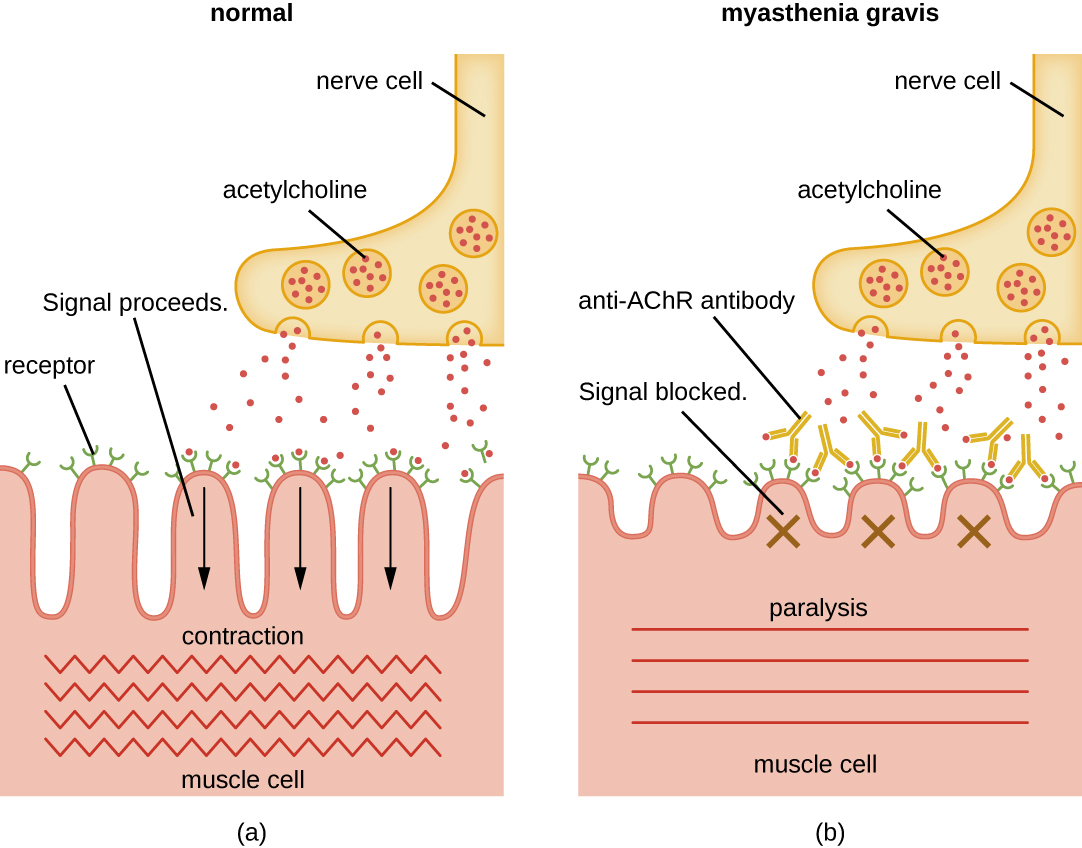
Autoantibodies directed against acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) in the synaptic cleft of neuromuscular junctions lead to myasthenia gravis ( [link] ). Anti-AChR antibodies are high-affinity IgGs and their synthesis requires activated CD4 T cells to interact with and stimulate B cells. Once produced, the anti-AChR antibodies affect neuromuscular transmission by at least three mechanisms:
Regardless of the mechanism, the effect of anti-AChR is extreme muscle weakness and potentially death through respiratory arrest in severe cases.
Psoriasis is a skin disease that causes itchy or sore patches of thick, red skin with silvery scales on elbows, knees, scalp, back, face, palms, feet, and sometimes other areas. Some individuals with psoriasis also get a form of arthritis called psoriatic arthritis , in which the joints can become inflamed. Psoriasis results from the complex interplay between keratinocytes, dendritic cells, and T cells, and the cytokines produced by these various cells. In a process called cell turnover, skin cells that grow deep in the skin rise to the surface. Normally, this process takes a month. In psoriasis, as a result of cytokine activation, cell turnover happens in just a few days. The thick inflamed patches of skin that are characteristic of psoriasis develop because the skin cells rise too fast.
The most common chronic inflammatory joint disease is rheumatoid arthritis (RA) ( [link] ) and it is still a major medical challenge because of unsolved questions related to the environmental and genetic causes of the disease. RA involves type III hypersensitivity reactions and the activation of CD4 T cells, resulting in chronic release of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1 , IL-6 , and tumor necrosis factor-α ( TNF-α ). The activated CD4 T cells also stimulate the production of rheumatoid factor (RF) antibodies and anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (anti-CCP) that form immune complex es. Increased levels of acute-phase proteins , such as C-reactive protein (CRP) , are also produced as part of the inflammatory process and participate in complement fixation with the antibodies on the immune complexes. The formation of immune complexes and reaction to the immune factors cause an inflammatory process in joints, particularly in the hands, feet, and legs. Diagnosis of RA is based on elevated levels of RF, anti-CCP, quantitative CRP, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (modified Westergren). In addition, radiographs, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging scans can identify joint damage, such as erosions, a loss of bone within the joint, and narrowing of joint space.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?