| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
At the beginning of this chapter, a famous experiment was described in which scientists synthesized amino acid s under conditions simulating those present on earth long before the evolution of life as we know it. These compounds are capable of bonding together in essentially any number, yielding molecules of essentially any size that possess a wide array of physical and chemical properties and perform numerous functions vital to all organisms. The molecules derived from amino acids can function as structural components of cells and subcellular entities, as sources of nutrients, as atom- and energy-storage reservoirs, and as functional species such as hormones, enzymes, receptors, and transport molecules.
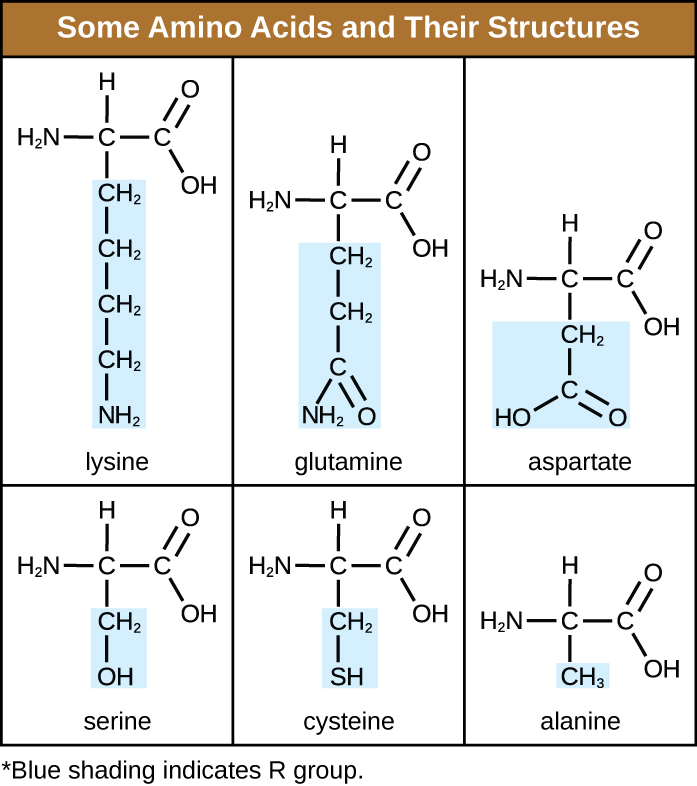
An amino acid is an organic molecule in which a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group (–COOH), and an amino group (–NH 2 ) are all bonded to the same carbon atom, the so-called α carbon . The fourth group bonded to the α carbon varies among the different amino acids and is called a residue or a side chain , represented in structural formulas by the letter R . A residue is a monomer that results when two or more amino acids combine and remove water molecules. The primary structure of a protein, a peptide chain, is made of amino acid residues. The unique characteristics of the functional groups and R group s allow these components of the amino acids to form hydrogen, ionic, and disulfide bonds, along with polar/nonpolar interactions needed to form secondary, tertiary, and quaternary protein structures. These groups are composed primarily of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur, in the form of hydrocarbons, acids, amides, alcohols, and amines. A few examples illustrating these possibilities are provided in [link] .
Amino acids may chemically bond together by reaction of the carboxylic acid group of one molecule with the amine group of another. This reaction forms a peptide bond and a water molecule and is another example of dehydration synthesis ( [link] ). Molecules formed by chemically linking relatively modest numbers of amino acid s (approximately 50 or fewer) are called peptide s, and prefixes are often used to specify these numbers: dipeptide s (two amino acids), tripeptide s (three amino acids), and so forth. More generally, the approximate number of amino acids is designated: oligopeptide s are formed by joining up to approximately 20 amino acids, whereas polypeptide s are synthesized from up to approximately 50 amino acids. When the number of amino acids linked together becomes very large, or when multiple polypeptides are used as building subunits, the macromolecules that result are called proteins . The continuously variable length (the number of monomers) of these biopolymers , along with the variety of possible R group s on each amino acid, allows for a nearly unlimited diversity in the types of proteins that may be formed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?