| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
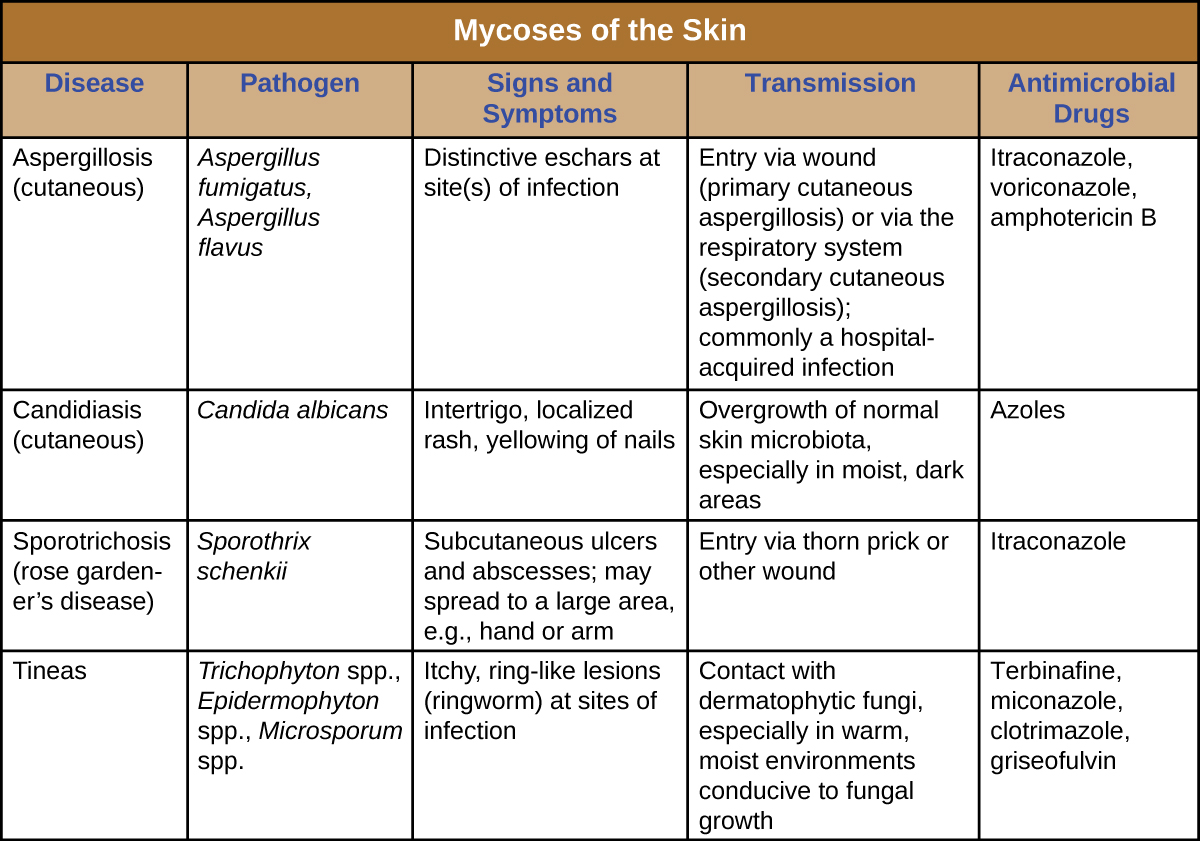
Cutaneous aspergillosis is diagnosed using patient history, culturing, histopathology using a skin biopsy. Treatment involves the use of antifungal medications such as voriconazole (preferred for invasive aspergillosis), itraconazole , and amphotericin B if itraconazole is not effective. For immunosuppressed individuals or burn patients, medication may be used and surgical or immunotherapy treatments may be needed.
Candida albicans and other yeasts in the genus Candida can cause skin infections referred to as cutaneous candidiasis. Candida spp. are sometimes responsible for intertrigo , a general term for a rash that occurs in a skin fold, or other localized rashes on the skin. Candida can also infect the nails, causing them to become yellow and harden ( [link] ).
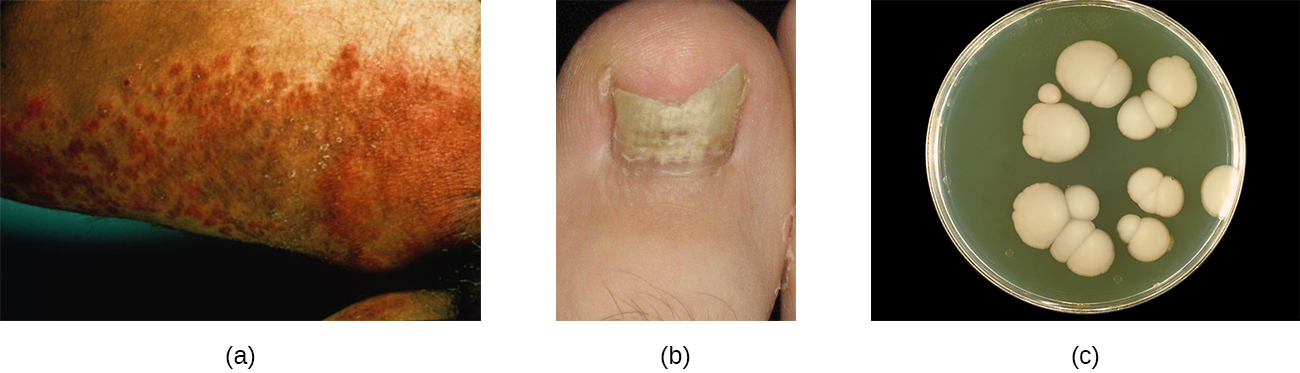
Candidiasis of the skin and nails is diagnosed through clinical observation and through culture, Gram stain, and KOH wet mounts. Susceptibility testing for anti-fungal agents can also be done. Cutaneous candidiasis can be treated with topical or systemic azole antifungal medications. Because candidiasis can become invasive, patients suffering from HIV/AIDS, cancer, or other conditions that compromise the immune system may benefit from preventive treatment. Azoles, such as clotrimazole , econazole , fluconazole , ketoconazole , and miconazole ; nystatin ; terbinafine ; and naftifine may be used for treatment. Long-term treatment with medications such as itraconazole or ketoconazole may be used for chronic infections. Repeat infections often occur, but this risk can be reduced by carefully following treatment recommendations, avoiding excessive moisture, maintaining good health, practicing good hygiene, and having appropriate clothing (including footwear).
Candida also causes infections in other parts of the body besides the skin. These include vaginal yeast infections (see Fungal Infections of the Reproductive System ) and oral thrush (see Microbial Diseases of the Mouth and Oral Cavity ).
Whereas cutaneous mycoses are superficial, subcutaneous mycoses can spread from the skin to deeper tissues. In temperate regions, the most common subcutaneous mycosis is a condition called sporotrichosis , caused by the fungus Sporothrix schenkii and commonly known as rose gardener’s disease or rose thorn disease (recall Case in Point: Every Rose Has Its Thorn ). Sporotrichosis is often contracted after working with soil, plants, or timber, as the fungus can gain entry through a small wound such as a thorn-prick or splinter. Sporotrichosis can generally be avoided by wearing gloves and protective clothing while gardening and promptly cleaning and disinfecting any wounds sustained during outdoor activities.
Sporothrix infections initially present as small ulcers in the skin, but the fungus can spread to the lymphatic system and sometimes beyond. When the infection spreads, nodules appear, become necrotic, and may ulcerate. As more lymph nodes become affected, abscesses and ulceration may develop over a larger area (often on one arm or hand). In severe cases, the infection may spread more widely throughout the body, although this is relatively uncommon.
Sporothrix infection can be diagnosed based upon histologic examination of the affected tissue. Its macroscopic morphology can be observed by culturing the mold on potato dextrose agar, and its microscopic morphology can be observed by staining a slide culture with lactophenol cotton blue. Treatment with itraconazole is generally recommended.
Cutaneous mycoses are typically opportunistic, only able to cause infection when the skin barrier is breached through a wound. Tineas are the exception, as the dermatophytes responsible for tineas are able to grow on skin, hair, and nails, especially in moist conditions. Most mycoses of the skin can be avoided through good hygiene and proper wound care. Treatment requires antifungal medications. [link] summarizes the characteristics of some common fungal infections of the skin.
The most common subcutaneous mycosis in temperate regions is ________.
sporotrichosis
What yeasts commonly cause opportunistic infections?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?