| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
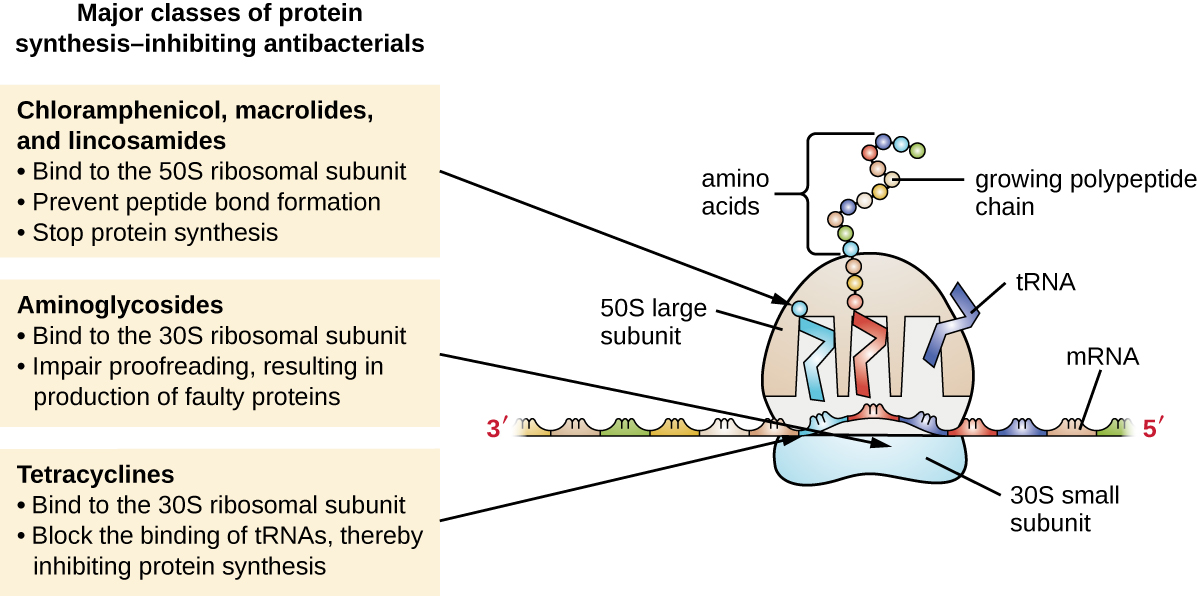
The lincosamides include the naturally produced lincomycin and semisynthetic clindamycin . Although structurally distinct from macrolides, lincosamides are similar in their mode of action to the macrolides through binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and preventing peptide bond formation. Lincosamides are particularly active against streptococcal and staphylococcal infections.
The drug chloramphenicol represents yet another structurally distinct class of antibacterials that also bind to the 50S ribosome, inhibiting peptide bond formation. Chloramphenicol, produced by Streptomyces venezuelae , was discovered in 1947; in 1949, it became the first broad-spectrum antibiotic that was approved by the FDA. Although it is a natural antibiotic, it is also easily synthesized and was the first antibacterial drug synthetically mass produced. As a result of its mass production, broad-spectrum coverage, and ability to penetrate into tissues efficiently, chloramphenicol was historically used to treat a wide range of infections, from meningitis to typhoid fever to conjunctivitis . Unfortunately, serious side effects, such as lethal gray baby syndrome , and suppression of bone marrow production, have limited its clinical role. Chloramphenicol also causes anemia in two different ways. One mechanism involves the targeting of mitochondrial ribosomes within hematopoietic stem cells, causing a reversible, dose-dependent suppression of blood cell production. Once chloramphenicol dosing is discontinued, blood cell production returns to normal. This mechanism highlights the similarity between 70S ribosomes of bacteria and the 70S ribosomes within our mitochondria. The second mechanism of anemia is idiosyncratic (i.e., the mechanism is not understood), and involves an irreversible lethal loss of blood cell production known as aplastic anemia . This mechanism of aplastic anemia is not dose dependent and can develop after therapy has stopped. Because of toxicity concerns, chloramphenicol usage in humans is now rare in the United States and is limited to severe infections unable to be treated by less toxic antibiotics. Because its side effects are much less severe in animals, it is used in veterinary medicine.
The oxazolidinones , including linezolid , are a new broad-spectrum class of synthetic protein synthesis inhibitors that bind to the 50S ribosomal subunit of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. However, their mechanism of action seems somewhat different from that of the other 50S subunit-binding protein synthesis inhibitors already discussed. Instead, they seem to interfere with formation of the initiation complex (association of the 50S subunit, 30S subunit, and other factors) for translation, and they prevent translocation of the growing protein from the ribosomal A site to the P site. [link] summarizes the protein synthesis inhibitors.
| Drugs That Inhibit Bacterial Protein Synthesis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Target | Mechanism of Action | Drug Class | Specific Drugs | Bacteriostatic or Bactericidal | Spectrum of Activity |
| 30S subunit | Causes mismatches between codons and anticodons, leading to faulty proteins that insert into and disrupt cytoplasmic membrane | Aminoglycosides | Streptomycin, gentamicin, neomycin, kanamycin | Bactericidal | Broad spectrum |
| Blocks association of tRNAs with ribosome | Tetracyclines | Tetracycline, doxycycline, tigecycline | Bacteriostatic | Broad spectrum | |
| 50S subunit | Blocks peptide bond formation between amino acids | Macrolides | Erythromycin, azithromycin, telithromycin | Bacteriostatic | Broad spectrum |
| Lincosamides | Lincomycin, clindamycin | Bacteriostatic | Narrow spectrum | ||
| Not applicable | Chloramphenicol | Bacteriostatic | Broad spectrum | ||
| Interferes with the formation of the initiation complex between 50S and 30S subunits and other factors. | Oxazolidinones | Linezolid | Bacteriostatic | Broad spectrum |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?