| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When society increases the level of capital per person, the result is called capital deepening . The idea of capital deepening can apply both to additional human capital per worker and to additional physical capital per worker.
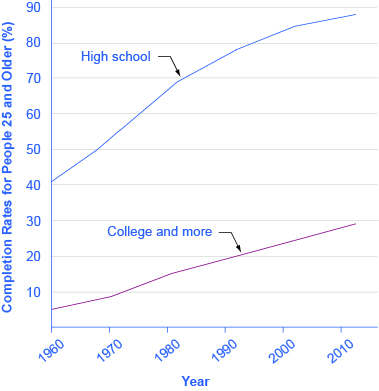
Recall that one way to measure human capital is to look at the average levels of education in an economy. [link] illustrates the human capital deepening for U.S. workers by showing that the proportion of the U.S. population with a high school and a college degree is rising. As recently as 1970, for example, only about half of U.S. adults had at least a high school diploma; by the start of the twenty-first century, more than 80% of adults had graduated from high school. The idea of human capital deepening also applies to the years of experience that workers have, but the average experience level of U.S. workers has not changed much in recent decades. Thus, the key dimension for deepening human capital in the U.S. economy focuses more on additional education and training than on a higher average level of work experience.
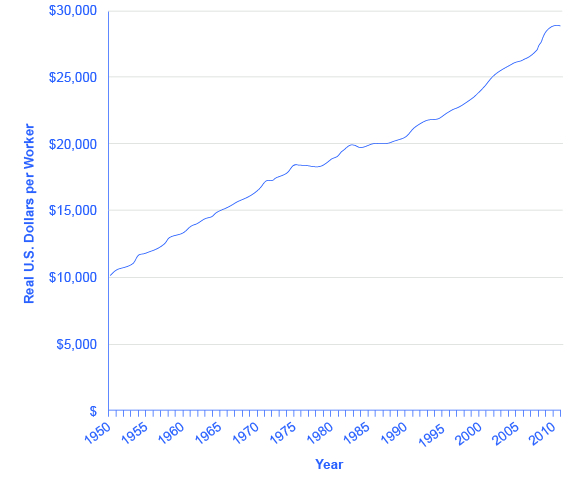
Physical capital deepening in the U.S. economy is shown in [link] . The average U.S. worker in the late 2000s was working with physical capital worth almost three times as much as that of the average worker of the early 1950s.
Not only does the current U.S. economy have better-educated workers with more and improved physical capital than it did several decades ago, but these workers have access to more advanced technologies. Growth in technology is impossible to measure with a simple line on a graph, but evidence that we live in an age of technological marvels is all around us—discoveries in genetics and in the structure of particles, the wireless Internet, and other inventions almost too numerous to count. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office typically has issued more than 150,000 patents annually in recent years.
This recipe for economic growth—investing in labor productivity, with investments in human capital and technology, as well as increasing physical capital—also applies to other economies. In South Korea, for example, universal enrollment in primary school (the equivalent of kindergarten through sixth grade in the United States) had already been achieved by 1965, when Korea’s GDP per capita was still near its rock bottom low. By the late 1980s, Korea had achieved almost universal secondary school education (the equivalent of a high school education in the United States). With regard to physical capital, Korea’s rates of investment had been about 15% of GDP at the start of the 1960s, but doubled to 30–35% of GDP by the late 1960s and early 1970s. With regard to technology, South Korean students went to universities and colleges around the world to get scientific and technical training, and South Korean firms reached out to study and form partnerships with firms that could offer them technological insights. These factors combined to foster South Korea’s high rate of economic growth.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?