| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Even after it became apparent that heterosexuals could contract the disease through blood transfusions and heterosexual intercourse, HIV/AIDS continued to be associated primarily with the gay community, especially by political and religious conservatives. Indeed, the Religious Right regarded it as a form of divine retribution meant to punish gay men for their “immoral” lifestyle. President Reagan, always politically careful, was reluctant to speak openly about the developing crisis even as thousands faced certain death from the disease.
With little help coming from the government, the gay community quickly began to organize its own response. In 1982, New York City men formed the Gay Men’s Health Crisis (GMHC), a volunteer organization that operated an information hotline, provided counseling and legal assistance, and raised money for people with HIV/AIDS. Larry Kramer, one of the original members, left in 1983 and formed his own organization, the AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power (ACT UP), in 1987. ACT UP took a more militant approach, holding demonstrations on Wall Street, outside the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and inside the New York Stock Exchange to call attention and shame the government into action. One of the images adopted by the group, a pink triangle paired with the phrase “Silence = Death,” captured media attention and quickly became the symbol of the AIDS crisis ( [link] ).

As Ronald Reagan took office in 1981, violent crime in the United States was reaching an all-time high. While there were different reasons for the spike, the most important one was demographics: The primary category of offenders, males between the ages of sixteen and thirty-six, reached an all-time peak as the baby-boomer generation came of age. But the phenomenon that most politicians honed in on as a cause for violent crime was the abuse of a new, cheap drug dealt illegally on city streets. Crack cocaine, a smokable type of cocaine popular with poorer addicts, was hitting the streets in the 1980s, frightening middle-class Americans. Reagan and other conservatives led a campaign to “get tough on crime” and promised the nation a “ war on drugs .” Initiatives like the “Just Say No” campaign led by First Lady Nancy Reagan implied that drug addiction and drug-related crime reflected personal morality.
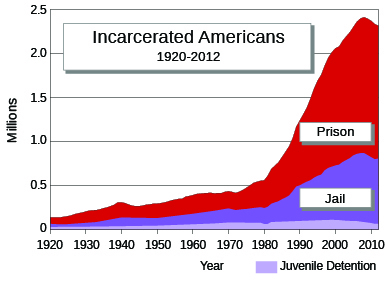
Nixon had first used the term in 1971, but in the 1980s the “war on drugs” took on an ominous dimension, as politicians scrambled over each other to enact harsher sentences for drug offenses so they could market themselves as tough on crime. State after state switched from variable to mandatory minimum sentences that were exceedingly long and particularly harsh for street drug crimes. The federal government supported the trend with federal sentencing guidelines and additional funds for local law enforcement agencies. This law-and-order movement peaked in the 1990s, when California introduced a “three strikes” law that mandated life imprisonment without parole for any third felony conviction—even nonviolent ones. As a result, prisons became crowded, and states went deep into debt to build more. By the end of the century, the war began to die down as the public lost interest in the problem, the costs of the punishment binge became politically burdensome, and scholars and politicians began to advocate the decriminalization of drug use. By this time, however, hundreds of thousands of people had been incarcerated for drug offenses and the total number of prisoners in the nation had grown four-fold in the last quarter of the century. Particularly glaring were the racial inequities of the new age of mass incarceration, with African Americans being seven times more likely to be in prison ( [link] ).
The political conservatism of the 1980s and 1990s was matched by the social conservatism of the period. Conservative politicians wished to limit the size and curb the power of the federal government. Conservative think tanks flourished, the Christian Right defeated the ERA, and bipartisan efforts to add warning labels to explicit music lyrics were the subject of Congressional hearings. HIV/AIDS, which became chiefly and inaccurately associated with the gay community, grew to crisis proportions, as heterosexuals and the federal government failed to act. In response, gay men organized advocacy groups to fight for research on HIV/AIDS. Meanwhile, the so-called war on drugs began a get-tough trend in law enforcement that mandated lengthy sentences for drug-related offenses and hugely increased the American prison population.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?