| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Unlike the South, however, which could hunker down to defend itself and needed to maintain relatively short supply lines, the North had to go forth and conquer. Union armies had to establish long supply lines, and Union soldiers had to fight on unfamiliar ground and contend with a hostile civilian population off the battlefield. Furthermore, to restore the Union—Lincoln’s overriding goal, in 1861—the United States, after defeating the Southern forces, would then need to pacify a conquered Confederacy, an area of over half a million square miles with nearly nine million residents. In short, although it had better resources and a larger population, the Union faced a daunting task against the well-positioned Confederacy.
The military forces of the Confederacy and the Union battled in 1861 and early 1862 without either side gaining the upper hand. The majority of military leaders on both sides had received the same military education and often knew one another personally, either from their time as students at West Point or as commanding officers in the Mexican-American War. This familiarity allowed them to anticipate each other’s strategies. Both sides believed in the use of concentrated armies charged with taking the capital city of the enemy. For the Union, this meant the capture of the Confederate capital in Richmond, Virginia, whereas Washington, DC, stood as the prize for Confederate forces. After hopes of a quick victory faded at Bull Run, the months dragged on without any major movement on either side ( [link] ).
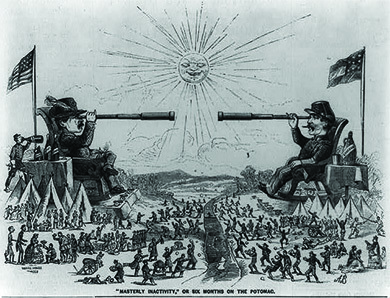
General George B. McClellan, the general in chief of the army, responsible for overall control of Union land forces, proved especially reluctant to engage in battle with the Confederates. In direct command of the Army of the Potomac , the Union fighting force operating outside Washington, DC, McClellan believed, incorrectly, that Confederate forces were too strong to defeat and was reluctant to risk his troops in battle. His cautious nature made him popular with his men but not with the president or Congress. By 1862, however, both President Lincoln and the new Secretary of War Edwin Stanton had tired of waiting. The Union put forward a new effort to bolster troop strength, enlisting one million men to serve for three-year stints in the Army of the Potomac. In January 1862, Lincoln and Stanton ordered McClellan to invade the Confederacy with the goal of capturing Richmond.
To that end, General McClellan slowly moved 100,000 soldiers of the Army of the Potomac toward Richmond but stopped a few miles outside the city. As he did so, a Confederate force led by Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson moved north to take Washington, DC. To fend off Jackson’s attack, somewhere between one-quarter and one-third of McClellan’s soldiers, led by Major General Irvin McDowell, returned to defend the nation’s capital, a move that Jackson hoped would leave the remaining troops near Richmond more vulnerable. Having succeeding in drawing off a sizable portion of the Union force, he joined General Lee to launch an attack on McClellan’s remaining soldiers near Richmond. From June 25 to July 1, 1862, the two sides engaged in the brutal Seven Days Battles that killed or wounded almost twenty thousand Confederate and ten thousand Union soldiers. McClellan’s army finally returned north, having failed to take Richmond.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?