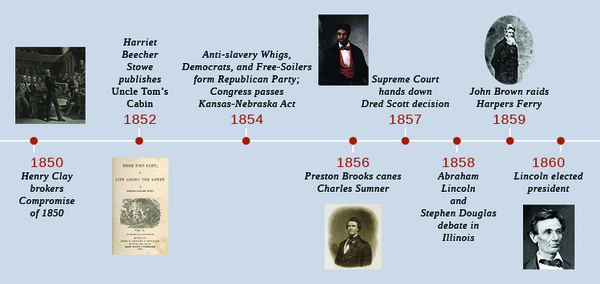
| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
At the end of the Mexican-American War, the United States gained a large expanse of western territory known as the Mexican Cession. The disposition of this new territory was in question; would the new states be slave states or free-soil states? In the long run, the Mexican-American War achieved what abolitionism alone had failed to do: it mobilized many in the North against slavery.
Antislavery northerners clung to the idea expressed in the 1846 Wilmot Proviso: slavery would not expand into the areas taken, and later bought, from Mexico. Though the proviso remained a proposal and never became a law, it defined the sectional division. The Free-Soil Party, which formed at the conclusion of the Mexican-American War in 1848 and included many members of the failed Liberty Party, made this position the centerpiece of all its political activities, ensuring that the issue of slavery and its expansion remained at the front and center of American political debate. Supporters of the Wilmot Proviso and members of the new Free-Soil Party did not want to abolish slavery in the states where it already existed; rather, Free-Soil advocates demanded that the western territories be kept free of slavery for the benefit of white laborers who might settle there. They wanted to protect white workers from having to compete with slave labor in the West. (Abolitionists, in contrast, looked to destroy slavery everywhere in the United States.) Southern extremists, especially wealthy slaveholders, reacted with outrage at this effort to limit slavery’s expansion. They argued for the right to bring their slave property west, and they vowed to leave the Union if necessary to protect their way of life—meaning the right to own slaves—and ensure that the American empire of slavery would continue to grow.
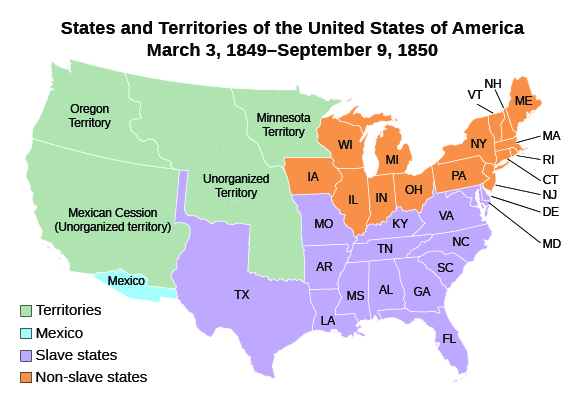
The issue of what to do with the western territories added to the republic by the Mexican Cession consumed Congress in 1850. Other controversial matters, which had been simmering over time, complicated the problem further. Chief among these issues were the slave trade in the District of Columbia, which antislavery advocates hoped to end, and the fugitive slave laws, which southerners wanted to strengthen. The border between Texas and New Mexico remained contested because many Texans hoped to enlarge their state further, and, finally, the issue of California had not been resolved. California was the crown jewel of the Mexican Cession, and following the discovery of gold, it was flush with thousands of emigrants. By most estimates, however, it would be a free state, since the former Mexican ban on slavery still remained in force and slavery had not taken root in California. The map below ( [link] ) shows the disposition of land before the 1850 compromise.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?