| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Congress has made numerous changes to the federal judicial system throughout the years, but the three-tiered structure of the system is quite clear-cut today. Federal cases typically begin at the lowest federal level, the district (or trial) court. Losing parties may appeal their case to the higher courts—first to the circuit courts, or U.S. courts of appeals, and then, if chosen by the justices, to the U.S. Supreme Court. Decisions of the higher courts are binding on the lower courts. The precedent set by each ruling, particularly by the Supreme Court’s decisions, both builds on principles and guidelines set by earlier cases and frames the ongoing operation of the courts, steering the direction of the entire system. Reliance on precedent has enabled the federal courts to operate with logic and consistency that has helped validate their role as the key interpreters of the Constitution and the law—a legitimacy particularly vital in the United States where citizens do not elect federal judges and justices but are still subject to their rulings.
There are ninety-four U.S. district courts in the fifty states and U.S. territories, of which eighty-nine are in the states (at least one in each state). The others are in Washington, DC; Puerto Rico; Guam; the U.S. Virgin Islands; and the Northern Mariana Islands. These are the trial courts of the national system, in which federal cases are tried, witness testimony is heard, and evidence is presented. No district court crosses state lines, and a single judge oversees each one. Some cases are heard by a jury, and some are not.
There are thirteen U.S. courts of appeals , or circuit courts , eleven across the nation and two in Washington, DC (the DC circuit and the federal circuit courts), as illustrated in [link] . Each court is overseen by a rotating panel of three judges who do not hold trials but instead review the rulings of the trial (district) courts within their geographic circuit. As authorized by Congress, there are currently 179 judges. The circuit courts are often referred to as the intermediate appellate courts of the federal system, since their rulings can be appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court. Moreover, different circuits can hold legal and cultural views, which can lead to differing outcomes on similar legal questions. In such scenarios, clarification from the U.S. Supreme Court might be needed.
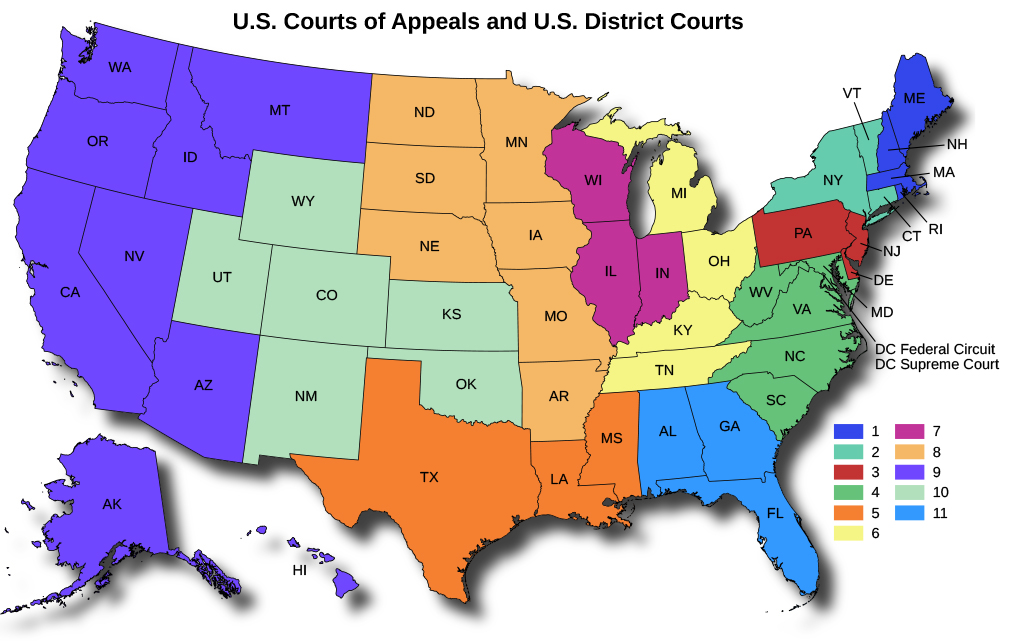
Today’s
federal court system was not an overnight creation; it has been changing and transitioning for more than two hundred years through various acts of Congress. Since district courts are not called for in
Article III of the Constitution, Congress established them and narrowly defined their jurisdiction, at first limiting them to handling only cases that arose within the district. Beginning in 1789 when there were just thirteen, the district courts became the basic organizational units of the federal judicial system. Gradually over the next hundred years, Congress expanded their jurisdiction, in particular over federal questions, which enables them to review constitutional issues and matters of federal law. In the
Judicial Code of 1911 , Congress made the U.S. district courts the sole general-jurisdiction trial courts of the federal judiciary, a role they had previously shared with the circuit courts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'American government' conversation and receive update notifications?