| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The origins of the U.S. Constitution and the convention that brought it into existence are rooted in failure—the failure of the Articles of Confederation. After only a handful of years, the states of the union decided that the Articles were simply unworkable. In order to save the young republic, a convention was called, and delegates were sent to assemble and revise the Articles. From the discussions and compromises in this convention emerged Congress in the form we recognize today. In this section, we will explore the debates and compromises that brought about the bicameral (two-chamber) Congress, made up of a House of Representatives and Senate. We will also explore the goals of bicameralism and how it functions. Finally, we will look at the different ways seats are apportioned in the two chambers.
Only a few years after the adoption of the Articles of Confederation, the republican experiment seemed on the verge of failure. States deep in debt were printing increasingly worthless paper currency, many were mired in interstate trade battles with each other, and in western Massachusetts, a small group of Revolutionary War veterans angry over the prospect of losing their farms broke into armed open revolt against the state, in what came to be known as Shays’ Rebellion. The conclusion many reached was that the Articles of Confederation were simply not strong enough to keep the young republic together. In the spring of 1787, a convention was called, and delegates from all the states (except Rhode Island, which boycotted the convention) were sent to Philadelphia to hammer out a solution to this central problem.
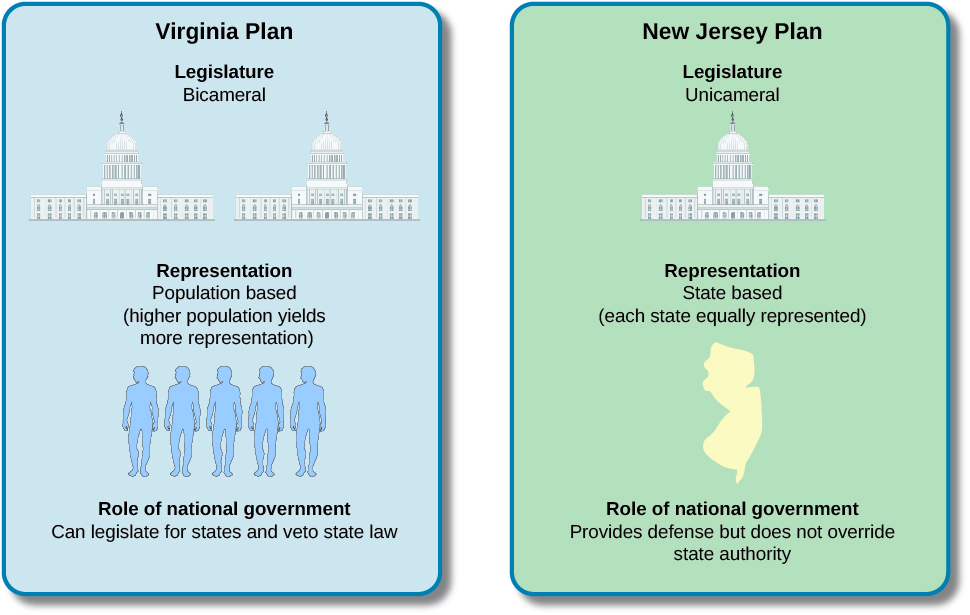
The meeting these delegates convened became known as the Constitutional Convention of 1787 . Although its prescribed purpose was to revise the Articles of Confederation, a number of delegates charted a path toward disposing of the Articles entirely. Under the Articles, the national legislature had been made up of a single chamber composed of an equal number of delegates from each of the states. Large states, like Virginia, felt it would be unfair to continue with this style of legislative institution. As a result, Virginia’s delegates proposed a plan that called for bicameralism , or the division of legislators into two separate assemblies. In this proposed two-chamber Congress, states with larger populations would have more representatives in each chamber. Predictably, smaller states like New Jersey were unhappy with this proposal. In response, they issued their own plan, which called for a single-chamber Congress with equal representation and more state authority ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'American government' conversation and receive update notifications?