| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
How does the macroeconomy adjust back to its level of potential GDP in the long run? What if aggregate demand increases or decreases? The neoclassical view of how the macroeconomy adjusts is based on the insight that even if wages and prices are “sticky”, or slow to change, in the short run, they are flexible over time. To understand this better, let's follow the connections from the short-run to the long-run macroeconomic equilibrium.
The aggregate demand and aggregate supply diagram shown in [link] shows two aggregate supply curves. The original upward sloping aggregate supply curve (SRAS 0 ) is a short-run or Keynesian AS curve. The vertical aggregate supply curve (LRASn) is the long-run or neoclassical AS curve, which is located at potential GDP. The original aggregate demand curve, labeled AD 0 , is drawn so that the original equilibrium occurs at point E 0 , at which point the economy is producing at its potential GDP.
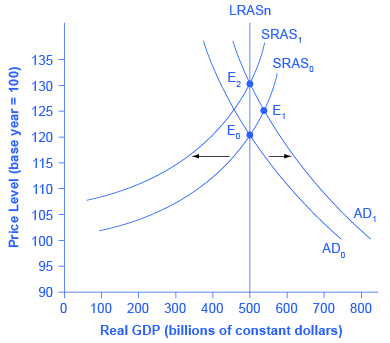
Now, imagine that some economic event boosts aggregate demand: perhaps a surge of export sales or a rise in business confidence that leads to more investment, perhaps a policy decision like higher government spending, or perhaps a tax cut that leads to additional aggregate demand. The short-run Keynesian analysis is that the rise in aggregate demand will shift the aggregate demand curve out to the right, from AD 0 to AD 1 , leading to a new equilibrium at point E 1 with higher output, lower unemployment, and pressure for an inflationary rise in the price level.
In the long-run neoclassical analysis, however, the chain of economic events is just beginning. As economic output rises above potential GDP, the level of unemployment falls. The economy is now above full employment and there is a shortage of labor. Eager employers are trying to bid workers away from other companies and to encourage their current workers to exert more effort and to put in longer hours. This high demand for labor will drive up wages. Most workers have their salaries reviewed only once or twice a year, and so it will take time before the higher wages filter through the economy. As wages do rise, it will mean a leftward shift in the short-run Keynesian aggregate supply curve back to SRAS 1 , because the price of a major input to production has increased. The economy moves to a new equilibrium (E 2 ). The new equilibrium has the same level of real GDP as did the original equilibrium (E 0 ), but there has been an inflationary increase in the price level.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?