| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Moreover, policies to diminish inequality and soften the hardship of poverty may sustain political support for a market economy. After all, if society does not make some effort toward reducing inequality and poverty, the alternative might be that people would rebel against market forces. Citizens might seek economic security by demanding that their legislators pass laws forbidding employers from ever laying off workers or reducing wages, or laws that would impose price floors and price ceilings and shut off international trade. From this viewpoint, policies to reduce inequality may help economic output by building social support for allowing markets to operate.
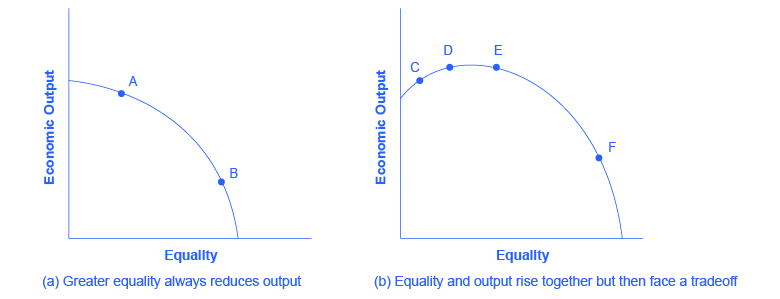
The tradeoff in [link] (b) then flattens out in the area between points D and E, which reflects the pattern that a number of countries that provide similar levels of income to their citizens—the United States, Canada, the nations of the European Union, Japan, Australia—have different levels of inequality. The pattern suggests that countries in this range could choose a greater or a lesser degree of inequality without much impact on economic output. Only if these countries push for a much higher level of equality, like at point F, will they experience the diminished incentives that lead to lower levels of economic output. In this view, while a danger always exists that an agenda to reduce poverty or inequality can be poorly designed or pushed too far, it is also possible to discover and design policies that improve equality and do not injure incentives for economic output by very much—or even improve such incentives.
The Occupy movement took on a life of its own over the last few months of 2011, bringing to light issues faced by many people on the lower end of the income distribution. The contents of this chapter indicate that there is a significant amount of income inequality in the United States. The question is: What should be done about it?
The Great Recession of 2008–2009 caused unemployment to rise and incomes to fall. Many people attribute the recession to mismanagement of the financial system by bankers and financial managers—those in the 1% of the income distribution—but those in lower quintiles bore the greater burden of the recession through unemployment. This seemed to present the picture of inequality in a different light: the group that seemed responsible for the recession was not the group that seemed to bear the burden of the decline in output. A burden shared can bring a society closer together; a burden pushed off onto others can polarize it.
On one level, the problem with trying to reduce income inequality comes down to whether you still believe in the American Dream. If you believe that one day you will have your American Dream—a large income, large house, happy family, or whatever else you would like to have in life—then you do not necessarily want to prevent anyone else from living out their dream. You certainly would not want to run the risk that someone would want to take part of your dream away from you. So there is some reluctance to engage in a redistributive policy to reduce inequality.
However, when those for whom the likelihood of living the American Dream is very small are considered, there are sound arguments in favor of trying to create greater balance. As the text indicated, a little more income equality, gained through long-term programs like increased education and job training, can increase overall economic output. Then everyone is made better off. And the 1% will not seem like such a small group any more.
Policies that can affect the level of economic inequality include redistribution between rich and poor, making it easier for people to climb the ladder of opportunity; and estate taxes, which are taxes on inheritances. Pushing too aggressively for economic equality can run the risk of decreasing economic incentives. However, a moderate push for economic equality can increase economic output, both through methods like improved education and by building a base of political support for market forces.
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. “Research Resources: Survey of Consumer Finances.” Last modified December 13, 2013. http://www.federalreserve.gov/econresdata/scf/scfindex.htm.
Congressional Budget Office. “The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2008 and 2009.” Last modified July 10, 2012. http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43373.
Huang, Chye-Ching, and Nathaniel Frentz. “Myths and Realities About the Estate Tax.” Center on Budget and Policy Priorities . Last modified August 29, 2013. http://www.cbpp.org/files/estatetaxmyths.pdf.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?