| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Visit this website for data on consumer confidence.
In the AD/AS diagram, cyclical unemployment is shown by how close the economy is to the potential or full employment level of GDP. Returning to [link] , relatively low cyclical unemployment for an economy occurs when the level of output is close to potential GDP, as in the equilibrium point E 1 . Conversely, high cyclical unemployment arises when the output is substantially to the left of potential GDP on the AD/AS diagram, as at the equilibrium point E 0 . The factors that determine the natural rate of unemployment are not shown separately in the AD/AS model, although they are implicitly part of what determines potential GDP or full employment GDP in a given economy.
Inflation fluctuates in the short run. Higher inflation rates have typically occurred either during or just after economic booms: for example, the biggest spurts of inflation in the U.S. economy during the twentieth century followed the wartime booms of World War I and World War II. Conversely, rates of inflation generally decline during recessions. As an extreme example, inflation actually became negative—a situation called “deflation”—during the Great Depression. Even during the relatively short recession of 1991–1992, the rate of inflation declined from 5.4% in 1990 to 3.0% in 1992. During the relatively short recession of 2001, the rate of inflation declined from 3.4% in 2000 to 1.6% in 2002. During the deep recession of 2007–2009, the rate of inflation declined from 3.8% in 2008 to –0.4% in 2009. Some countries have experienced bouts of high inflation that lasted for years. In the U.S. economy since the mid–1980s, inflation does not seem to have had any long-term trend to be substantially higher or lower; instead, it has stayed in the range of 1–5% annually.
Visit this website for data on business confidence.

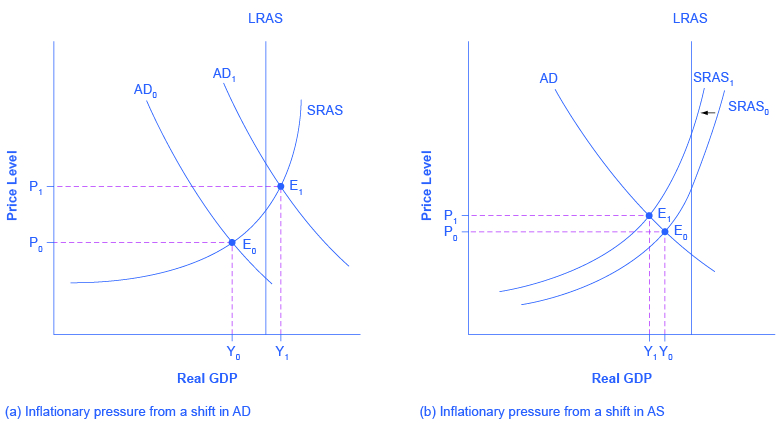
The AD/AS framework implies two ways that inflationary pressures may arise. One possible trigger is if aggregate demand continues to shift to the right when the economy is already at or near potential GDP and full employment, thus pushing the macroeconomic equilibrium into the steep portion of the AS curve. In [link] (a), there is a shift of aggregate demand to the right; the new equilibrium E 1 is clearly at a higher price level than the original equilibrium E 0 . In this situation, the aggregate demand in the economy has soared so high that firms in the economy are not capable of producing additional goods, because labor and physical capital are fully employed, and so additional increases in aggregate demand can only result in a rise in the price level.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?