| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Quantity | Marginal Revenue | Marginal Cost | Marginal Profit | Total Profit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,200 | 1,500 | –300 | –300 |
| 2 | 1,000 | 300 | 700 | 400 |
| 3 | 800 | 400 | 400 | 800 |
| 4 | 600 | 600 | 0 | 800 |
| 5 | 400 | 700 | –300 | 500 |
| 6 | 200 | 700 | –500 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 1,400 | –1,400 | –1,400 |
[link] repeats the marginal cost and marginal revenue data from [link] , and adds two more columns: Marginal profit is the profitability of each additional unit sold. It is defined as marginal revenue minus marginal cost. Finally, total profit is the sum of marginal profits. As long as marginal profit is positive, producing more output will increase total profits. When marginal profit turns negative, producing more output will decrease total profits. Total profit is maximized where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. In this example, maximum profit occurs at 4 units of output.
A perfectly competitive firm will also find its profit-maximizing level of output where MR = MC. The key difference with a perfectly competitive firm is that in the case of perfect competition, marginal revenue is equal to price (MR = P), while for a monopolist, marginal revenue is not equal to the price, because changes in quantity of output affect the price.
It is straightforward to calculate profits of given numbers for total revenue and total cost. However, the size of monopoly profits can also be illustrated graphically with [link] , which takes the marginal cost and marginal revenue curves from the previous exhibit and adds an average cost curve and the monopolist’s perceived demand curve.
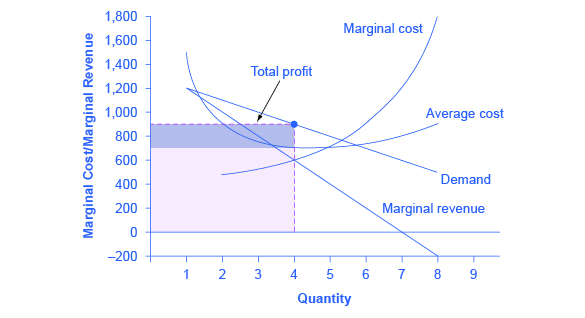
[link] illustrates the three-step process where a monopolist: selects the profit-maximizing quantity to produce; decides what price to charge; determines total revenue, total cost, and profit.
Step 1: The Monopolist Determines Its Profit-Maximizing Level of Output
The firm can use the points on the demand curve D to calculate total revenue, and then, based on total revenue, calculate its marginal revenue curve. The profit-maximizing quantity will occur where MR = MC—or at the last possible point before marginal costs start exceeding marginal revenue. On [link] , MR = MC occurs at an output of 4.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?