| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Elasticity also reveals whether firms can pass higher costs that they incur on to consumers. Addictive substances tend to fall into this category. For example, the demand for cigarettes is relatively inelastic among regular smokers who are somewhat addicted; economic research suggests that increasing the price of cigarettes by 10% leads to about a 3% reduction in the quantity of cigarettes smoked by adults, so the elasticity of demand for cigarettes is 0.3. If society increases taxes on companies that make cigarettes, the result will be, as in [link] (a), that the supply curve shifts from S 0 to S 1 . However, as the equilibrium moves from E 0 to E 1 , these taxes are mainly passed along to consumers in the form of higher prices. These higher taxes on cigarettes will raise tax revenue for the government, but they will not much affect the quantity of smoking.
If the goal is to reduce the quantity of cigarettes demanded, it must be achieved by shifting this inelastic demand back to the left, perhaps with public programs to discourage the use of cigarettes or to help people to quit. For example, anti-smoking advertising campaigns have shown some ability to reduce smoking. However, if demand for cigarettes was more elastic, as in [link] (b), then an increase in taxes that shifts supply from S 0 to S 1 and equilibrium from E 0 to E 1 would reduce the quantity of cigarettes smoked substantially. Youth smoking seems to be more elastic than adult smoking—that is, the quantity of youth smoking will fall by a greater percentage than the quantity of adult smoking in response to a given percentage increase in price.
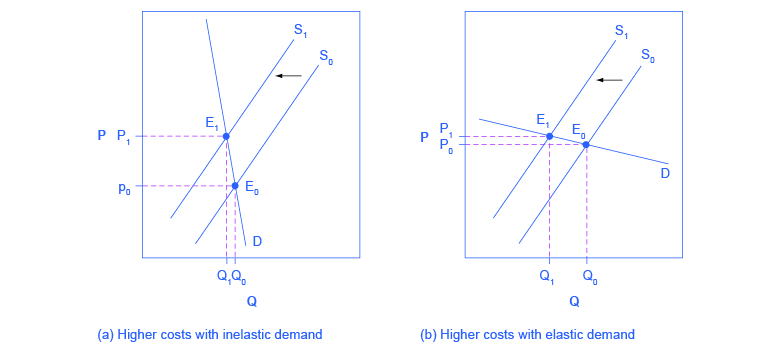
The example of cigarette taxes showed that because demand is inelastic, taxes are not effective at reducing the equilibrium quantity of smoking, and they are mainly passed along to consumers in the form of higher prices. The analysis, or manner, of how the burden of a tax is divided between consumers and producers is called tax incidence . Typically, the incidence, or burden, of a tax falls both on the consumers and producers of the taxed good. But if one wants to predict which group will bear most of the burden, all one needs to do is examine the elasticity of demand and supply. In the tobacco example, the tax burden falls on the most inelastic side of the market.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?