| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Traditional economists also assume human beings have complete self-control. But, for instance, people will buy cigarettes by the pack instead of the carton even though the carton saves them money, to keep usage down. They purchase locks for their refrigerators and overpay on taxes to force themselves to save. In other words, we protect ourselves from our worst temptations but pay a price to do so. One way behavioral economists are responding to this is by setting up ways for people to keep themselves free of these temptations. This includes what are called “nudges” toward more rational behavior rather than mandatory regulations from government. For example, up to 20 percent of new employees do not enroll in retirement savings plans immediately, because of procrastination or feeling overwhelmed by the different choices. Some companies are now moving to a new system, where employees are automatically enrolled unless they “opt out.” Almost no-one opts out in this program and employees begin saving at the early years, which are most critical for retirement.
Another area that seems illogical is the idea of mental accounting, or putting dollars in different mental categories where they take different values. Economists typically consider dollars to be fungible , or having equal value to the individual, regardless of the situation.
You might, for instance, think of the $25 you found in the street differently from the $25 you earned from three hours working in a fast food restaurant. The street money might well be treated as “mad money” with little rational regard to getting the best value. This is in one sense strange, since it is still equivalent to three hours of hard work in the restaurant. Yet the “easy come-easy go” mentality replaces the rational economizer because of the situation, or context, in which the money was attained.
In another example of mental accounting that seems inconsistent to a traditional economist, a person could carry a credit card debt of $1,000 that has a 15% yearly interest cost, and simultaneously have a $2,000 savings account that pays only 2% per year. That means she pays $150 a year to the credit card company, while collecting only $40 annually in bank interest, so she loses $130 a year. That doesn’t seem wise.
The “rational” decision would be to pay off the debt, since a $1,000 savings account with $0 in debt is the equivalent net worth, and she would now net $20 per year. But curiously, it is not uncommon for people to ignore this advice, since they will treat a loss to their savings account as higher than the benefit of paying off their credit card. The dollars are not being treated as fungible so it looks irrational to traditional economists.
Which view is right, the behavioral economists’ or the traditional view? Both have their advantages, but behavioral economists have at least shed a light on trying to describe and explain behavior that has historically been dismissed as irrational. If most of us are engaged in some “irrational behavior,” perhaps there are deeper underlying reasons for this behavior in the first place.
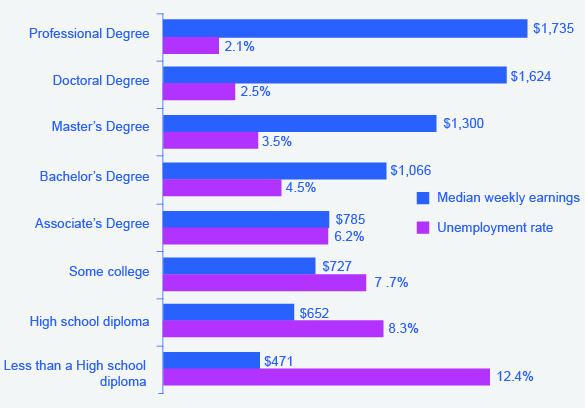
In what category did consumers worldwide increase their spending during the recession? Higher education. According to the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), enrollment in colleges and universities rose one-third in China and almost two-thirds in Saudi Arabia, nearly doubled in Pakistan, tripled in Uganda, and surged by three million—18 percent—in the United States. Why were consumers willing to spend on education during lean times? Both individuals and countries view higher education as the way to prosperity. Many feel that increased earnings are a significant benefit of attending college.
Bureau of Labor Statistics data from May 2012 supports this view, as shown in [link] . They show a positive correlation between earnings and education. The data also indicate that unemployment rates fall with higher levels of education and training.
When making a choice along the intertemporal budget constraint, a household will choose the combination of present consumption, savings, and future consumption that provides the most utility. The result of a higher rate of return (or higher interest rates) can be a higher quantity of saving, the same quantity of saving, or a lower quantity of saving, depending on preferences about present and future consumption. Behavioral economics is a branch of economics that seeks to understand and explain the "human" factors that drive what traditional economists see as people's irrational spending decisions.
Holden, Sarah, and Daniel Schrass. 2012. “The rose of IRAs in U.S Households’ Saving for Retirement, 2012.” ICI Research Perspective 18.8 (2012). http://www.ici.org/pdf/per18-08.pdf.
Kahneman, Daniel and Amos Tversky. “Prospect Theory: An Analysis of Decision under Risk.” Econometrica 47.2 (March 1979) 263-291.
Thaler, Richard H. “Shifting Our Retirement Savings into Automatic.” The New York Times , April 6, 2013. http://www.nytimes.com/2013/04/07/business/an-automatic-solution-for-the-retirement-savings-problem.html?pagewanted=all.
UNESCO Institute for Statistics. “Statistics in Brief / Profiles” Accessed August 2013. http://stats.uis.unesco.org/unesco/TableViewer/document.aspx?ReportId=121&IF_Language=en&BR_Country=5580.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?