| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
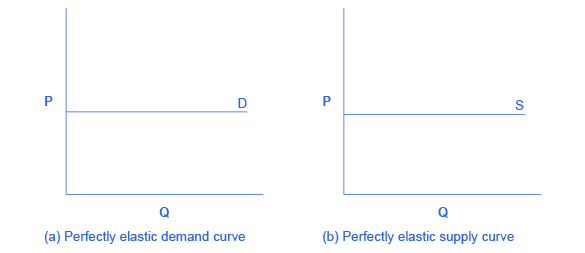
There are two extreme cases of elasticity: when elasticity equals zero and when it is infinite. A third case is that of constant unitary elasticity. We will describe each case. Infinite elasticity or perfect elasticity refers to the extreme case where either the quantity demanded (Qd) or supplied (Qs) changes by an infinite amount in response to any change in price at all. In both cases, the supply and the demand curve are horizontal as shown in [link] . While perfectly elastic supply curves are unrealistic, goods with readily available inputs and whose production can be easily expanded will feature highly elastic supply curves. Examples include pizza, bread, books and pencils. Similarly, perfectly elastic demand is an extreme example. But luxury goods, goods that take a large share of individuals’ income, and goods with many substitutes are likely to have highly elastic demand curves. Examples of such goods are Caribbean cruises and sports vehicles.
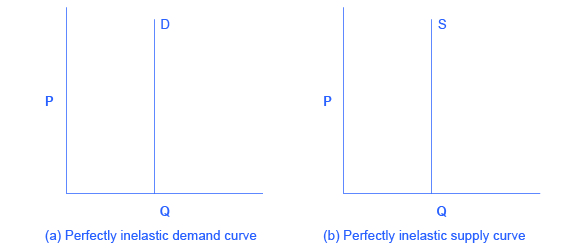
Zero elasticity or perfect inelasticity , as depicted in [link] refers to the extreme case in which a percentage change in price, no matter how large, results in zero change in quantity. While a perfectly inelastic supply is an extreme example, goods with limited supply of inputs are likely to feature highly inelastic supply curves. Examples include diamond rings or housing in prime locations such as apartments facing Central Park in New York City. Similarly, while perfectly inelastic demand is an extreme case, necessities with no close substitutes are likely to have highly inelastic demand curves. This is the case of life-saving drugs and gasoline.
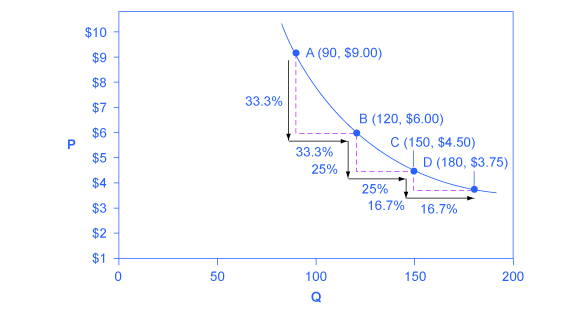
Constant unitary elasticity , in either a supply or demand curve, occurs when a price change of one percent results in a quantity change of one percent. [link] shows a demand curve with constant unit elasticity. As we move down the demand curve from A to B, the price falls by 33% and quantity demanded rises by 33%; as you move from B to C, the price falls by 25% and the quantity demanded rises by 25%; as you move from C to D, the price falls by 16% and the quantity rises by 16%. Notice that in absolute value, the declines in price, as you step down the demand curve, are not identical. Instead, the price falls by $3 from A to B, by a smaller amount of $1.50 from B to C, and by a still smaller amount of $0.75 from C to D. As a result, a demand curve with constant unitary elasticity moves from a steeper slope on the left and a flatter slope on the right—and a curved shape overall.
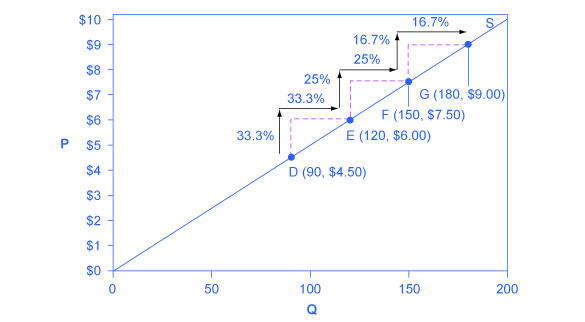
Unlike the demand curve with unitary elasticity, the supply curve with unitary elasticity is represented by a straight line. In moving up the supply curve from left to right, each increase in quantity of 30, from 90 to 120 to 150 to 180, is equal in absolute value. However, in percentage value, the steps are decreasing, from 33.3% to 25% to 16.7%, because the original quantity points in each percentage calculation are getting larger and larger, which expands the denominator in the elasticity calculation.
Consider the price changes moving up the supply curve in [link] . From points D to E to F and to G on the supply curve, each step of $1.50 is the same in absolute value. However, if the price changes are measured in percentage change terms, they are also decreasing, from 33.3% to 25% to 16.7%, because the original price points in each percentage calculation are getting larger and larger in value. Along the constant unitary elasticity supply curve, the percentage quantity increases on the horizontal axis exactly match the percentage price increases on the vertical axis—so this supply curve has a constant unitary elasticity at all points.
Infinite or perfect elasticity refers to the extreme case where either the quantity demanded or supplied changes by an infinite amount in response to any change in price at all. Zero elasticity refers to the extreme case in which a percentage change in price, no matter how large, results in zero change in quantity. Constant unitary elasticity in either a supply or demand curve refers to a situation where a price change of one percent results in a quantity change of one percent.
The supply of paintings by Leonardo Da Vinci, who painted the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper and died in 1519, is highly inelastic. Sketch a supply and demand diagram, paying attention to the appropriate elasticities, to illustrate that demand for these paintings will determine the price.
Say that a certain stadium for professional football has 70,000 seats. What is the shape of the supply curve for tickets to football games at that stadium? Explain.
When someone’s kidneys fail, the person needs to have medical treatment with a dialysis machine (unless or until they receive a kidney transplant) or they will die. Sketch a supply and demand diagram, paying attention to the appropriate elasticities, to illustrate that the supply of such dialysis machines will primarily determine the price.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?