| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Having discussed the revenue (taxes) and expense (spending) side of the budget, we now turn to the annual budget deficit or surplus, which is the difference between the tax revenue collected and spending over a fiscal year, which starts October 1 and ends September 30 of the next year.
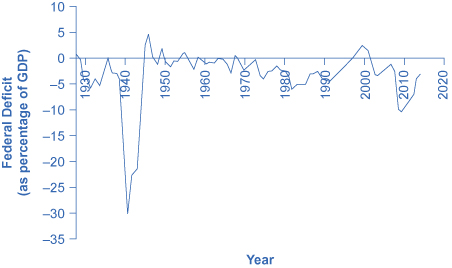
[link] shows the pattern of annual federal budget deficits and surpluses, back to 1930, as a share of GDP. When the line is above the horizontal axis, the budget is in surplus; when the line is below the horizontal axis, a budget deficit occurred. Clearly, the biggest deficits as a share of GDP during this time were incurred to finance World War II. Deficits were also large during the 1930s, the 1980s, the early 1990s, and most recently during the recession of 2008–2009.
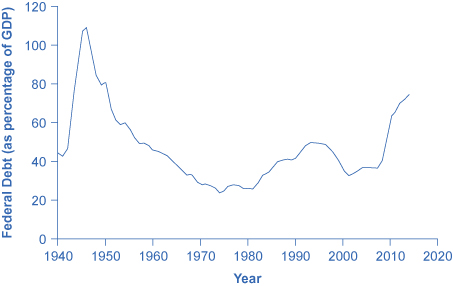
Another useful way to view the budget deficit is through the prism of accumulated debt rather than annual deficits. The national debt refers to the total amount that the government has borrowed over time; in contrast, the budget deficit refers to how much has been borrowed in one particular year. [link] shows the ratio of debt/GDP since 1940. Until the 1970s, the debt/GDP ratio revealed a fairly clear pattern of federal borrowing. The government ran up large deficits and raised the debt/GDP ratio in World War II, but from the 1950s to the 1970s the government ran either surpluses or relatively small deficits, and so the debt/GDP ratio drifted down. Large deficits in the 1980s and early 1990s caused the ratio to rise sharply. When budget surpluses arrived from 1998 to 2001, the debt/GDP ratio declined substantially. The budget deficits starting in 2002 then tugged the debt/GDP ratio higher—with a big jump when the recession took hold in 2008–2009.
The next Clear it Up feature discusses how the government handles the national debt.
One year’s federal budget deficit causes the federal government to sell Treasury bonds to make up the difference between spending programs and tax revenues. The dollar value of all the outstanding Treasury bonds on which the federal government owes money is equal to the national debt.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?