| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
After reading this module, students should be able to
You're probably familiar with the word, biodiversity , whether or not you can give an exact definition of it. It's common on the signs at zoos, parks, and nature centers, and it's often used without explanation or definition. Most people understand biodiversity in general terms as the number and mix of plant and animal species that occurs in a given place. Scientists are more precise and include more in their definition. The International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) , which coordinates efforts to catalogue and preserve biodiversity worldwide, defines biodiversity as "the variability among living organisms from all sources including terrestrial, marine and other aquatic ecosystems, and the ecological complexes of which they are part; this includes diversity within species, between species, and of ecosystems." Rather than just species, biodiversity therefore includes variation from the level of genes and genomes to that of ecosystems to biomes.
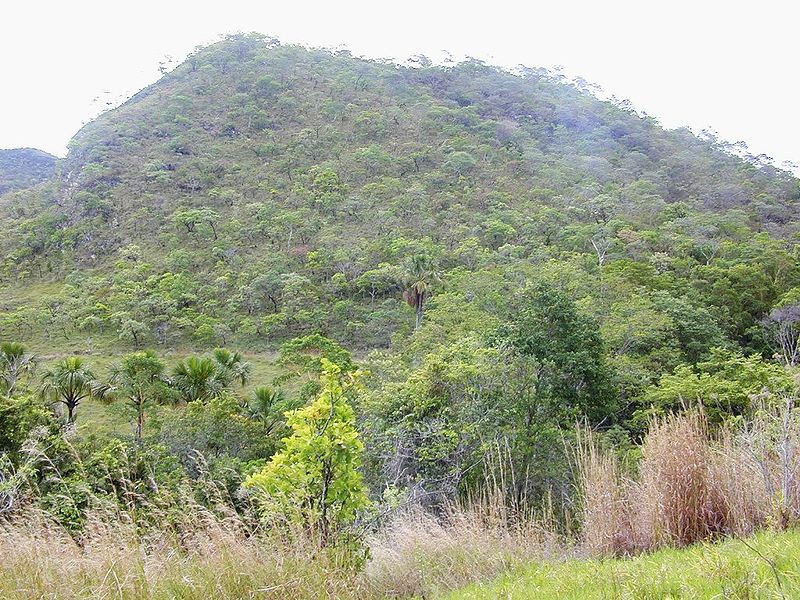
Even within a single ecosystem, the numbers of species can be impressive. For example, there is a large region of dry forest and savanna in Brazil known as the Cerrado (see Figure Cerrado Forest ). This ecosystem alone hosts over 10,000 species of plants, almost 200 species of mammals, over 600 species of birds, and about 800 species of fish.

Generally, biodiversity is greatest in tropical areas–especially "rainforests"—but there are terrestrial biodiversity "hotspots" on all the major continents. (View an interactive map of hotspots .)
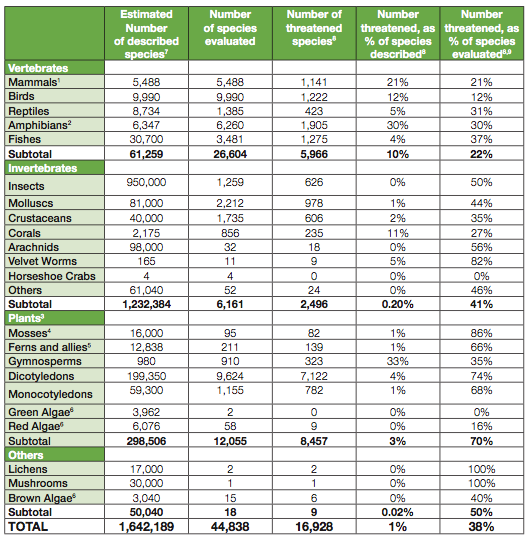
One way scientists gauge trends in biodiversity is by monitoring the fate of individual species of animals and plants. For more than 40 years, the IUCN has compiled information in the "Red List of Threatened Species," which "provides a snapshot of what is happening to species around the world." Updates to the Red List are released every four years. Here is how the authors of the most recent one, released in 2008, characterize the news it holds: "The overwhelming message" from the 2008 Red List, they write, "is that the world is losing species and that the rate of loss appears to be accelerating in many taxonomic groups" ( Vie, Hilton-Taylor,&Stuart, 2008, p. 38 ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?