| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Any foods that are found to be spoilt should be disposed of immediately, and products in the same lot should be inspected.
Disease-causing, pathogenic microorganisms can cause illnesses that can range from mild to life-threatening. These microorganisms are the most serious, so you must develop procedures to eliminate the risk of their contaminating products.
Examples of these microorganisms that should be effectively controlled are bacteria such as Salmonella or E. coli 0157:H7. The common symptoms of these are nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, and, in serious cases, death.
Pathogens are microorganisms that cause food-borne illness. Pathogens come in three forms:
Pathogens can be found in soils; these include:
The presence of pathogens within humans is the main reason why washing your hands after using the toilet is essential when working with food.
Bacteria are very resilient microorganisms that are found everywhere. Some examples of where they can live and multiply are
Because of the nature and diversity of bacteria, they can be found almost anywhere in your factory. It is, therefore, imperative that bacteria and other microorganisms are controlled to acceptable levels and, in some cases, completely eliminated in the food.
The problem with bacteria when concerned with food safety is that they are single- celled organisms that can live independently. When the conditions are correct, they can divide and multiply very quickly, as is seen in the example below. To multiply, bacteria need moisture, nutrients, warmth, and time. Moisture and nutrients are found on most foods, so bacterial growth on foods is very common.
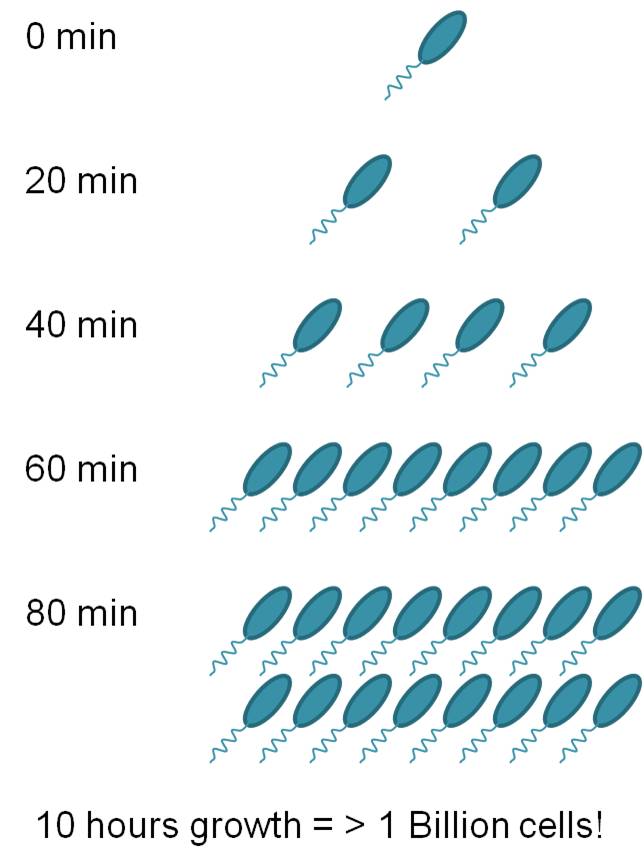
Bacteria cause the greatest number of deaths from food-borne illnesses. They are impossible to see with the naked eye. Taking these factors into account, it is clear that controlling bacteria can be difficult but is essential.
Viruses are different from bacteria since they do not multiply in food. They are intracellular organisms which invade living cells and then use the cell’s content to replicate.
Since viruses do not multiply on food, they contaminate by human or animal interaction. Food-borne viral disease generally results from poor personal hygiene or lack of pest control.
Viruses can also survive and travel in water and ice, so it is essential that your water supply is adequate, safe, and regularly monitored.
Personal hygiene for food handlers is extremely important in controlling viruses. All staff must be made aware of inappropriate personal hygiene practices, and monitoring should take place to ensure good personal hygiene is being followed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Food safety knowledge network basic level requirements' conversation and receive update notifications?