| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Why are unit vector fields important? Suppose we are studying the flow of a fluid, and we care only about the direction in which the fluid is flowing at a given point. In this case, the speed of the fluid (which is the magnitude of the corresponding velocity vector) is irrelevant, because all we care about is the direction of each vector. Therefore, the unit vector field associated with velocity is the field we would study.
If is a vector field, then the corresponding unit vector field is Notice that if is the vector field from [link] , then the magnitude of F is and therefore the corresponding unit vector field is the field G from the previous example.
If F is a vector field, then the process of dividing F by its magnitude to form unit vector field is called normalizing the field F .
We have seen several examples of vector fields in let’s now turn our attention to vector fields in These vector fields can be used to model gravitational or electromagnetic fields, and they can also be used to model fluid flow or heat flow in three dimensions. A two-dimensional vector field can really only model the movement of water on a two-dimensional slice of a river (such as the river’s surface). Since a river flows through three spatial dimensions, to model the flow of the entire depth of the river, we need a vector field in three dimensions.
The extra dimension of a three-dimensional field can make vector fields in more difficult to visualize, but the idea is the same. To visualize a vector field in plot enough vectors to show the overall shape. We can use a similar method to visualizing a vector field in by choosing points in each octant.
Just as with vector fields in we can represent vector fields in with component functions. We simply need an extra component function for the extra dimension. We write either
or
Describe vector field
For this vector field, the x and y components are constant, so every point in has an associated vector with x and y components equal to one. To visualize F , we first consider what the field looks like in the xy -plane. In the xy -plane, Hence, each point of the form has vector associated with it. For points not in the xy -plane but slightly above it, the associated vector has a small but positive z component, and therefore the associated vector points slightly upward. For points that are far above the xy -plane, the z component is large, so the vector is almost vertical. [link] shows this vector field.
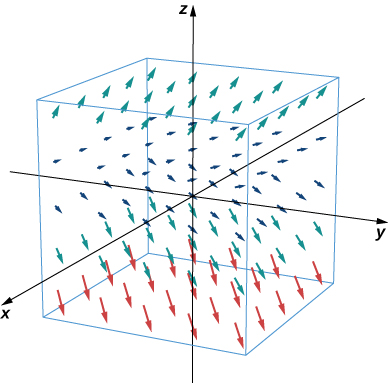
In the next example, we explore one of the classic cases of a three-dimensional vector field: a gravitational field.
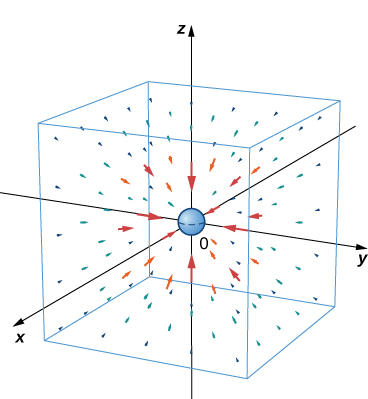
Newton’s law of gravitation states that where G is the universal gravitational constant. It describes the gravitational field exerted by an object (object 1) of mass located at the origin on another object (object 2) of mass located at point Field F denotes the gravitational force that object 1 exerts on object 2, r is the distance between the two objects, and indicates the unit vector from the first object to the second. The minus sign shows that the gravitational force attracts toward the origin; that is, the force of object 1 is attractive. Sketch the vector field associated with this equation.
Since object 1 is located at the origin, the distance between the objects is given by The unit vector from object 1 to object 2 is and hence Therefore, gravitational vector field F exerted by object 1 on object 2 is
This is an example of a radial vector field in
[link] shows what this gravitational field looks like for a large mass at the origin. Note that the magnitudes of the vectors increase as the vectors get closer to the origin.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?