| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Land use
You have discovered by now that your town, suburb, residential area or city is divided into different parts. The area where most of the shops or offices are located, is called the central business core (with businesses, shops and offices). Then there is the industrial area (factories and workshops) and the residential areas (houses and flats). There is a good reason for this division because it would not be acceptable to live next to a factory with all its noise and activities.
What types of buildings do we find in these areas? Fill in the table.
| Central business core | Industrial area | Residential area |
People who are responsible for designing towns and cities, are called town planners. Apart from determining where suburbs, industrial areas and the central business core should be situated, they must also see that land is made available for churches, schools, recreational areas, sports fields, streets, parking areas, and services such as railway lines, electricity supply, telephone communication, sewerage, etc. There are many aspects that town planners must keep in mind.
On official town or city maps land utilization is indicated in different colours. By means of the various colours, we can determine whether a specific section is used as an area for living or for industrial use.
This table indicates which colours should be used for the different areas on a land utilization map. Colour the table in the prescribed colours and then colour in the land utilization map in the correct colours.
| 1. | Business Sector | (dark blue) | ||
| 2. | Industrial Area | (purple) | ||
| 3. | High density occupation | (orange) | ||
| (not numbered) | Single occupation | (yellow) | ||
| 5. | Sports and recreation | (dark green) | ||
| 6. | Public open space | (light green) | ||
| 7. | Agricultural land | (dark green outline) | ||
| 8. | Schools | (grey) | ||
| 9. | Churches | (grey // 45 o black shading) |
L and U se M ap
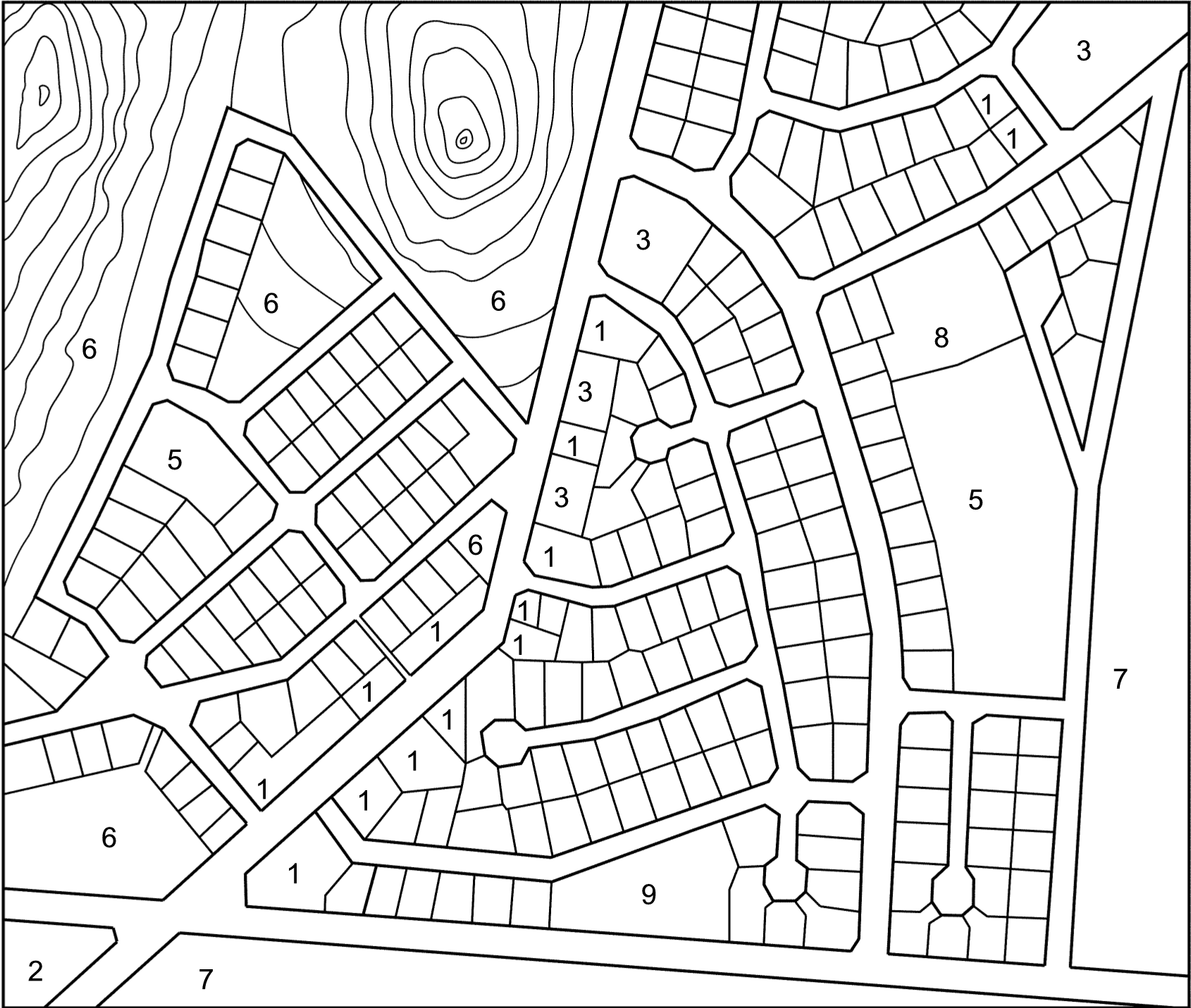
Explanation : To help you to identify land utilization, numbers are used.
All the plots without numbers are for general occupancy (residential areas).
Make a copy of a street plan of your town or suburb, e.g. the area where your school or home is located. Use only a section of the map. Use the same colours as for the previous activity and complete the land utilization map.
Go for a walk through your town, or try to do it the way you remember it, or from your discussion as a group.
After you have completed your map, you can compare it with a friend’s map.
Compile the rules that will make it pleasant for people who visit the area.
1. ………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
2. ………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
3. ………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
4. ………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
5. ………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
6. ………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
7. ……………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………….
8. ……………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………….
9. ……………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………….
10. ………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………
The learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate geographical and
environmental concepts and processes.
Assessment Standard
We know this when the learner:
1.1 identifies information from various sources (maps, atlases, books);
1.3 identifies symbols used in different kinds of maps (including plan view, grids and map keys) [works with sources];
1.7 uses geographical and environmental concepts and terms to report on enquiries in different ways (e.g. writing a paragraph, using a poster, artwork).
The learner will be able to demonstrate geographical and environmental knowledge and understanding.
We know this when the learner:
2.3 describes how basic human needs were met in the past and at present.
Land use
The different areas in a town/city
| Central business core | Industrial area | Residential area |
| Large office complexes | Large factories | Flats |
| Shopping centres | Smaller storage places | Houses |
| Businesses | Workshops | Townhouses |
| Storage places |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Geography grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?