| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
SPEAKING
It is impossible to imagine life on earth without the sun. Just try to picture what it would be like. It would be like living in a deep, dark cave: no night and day; no beautiful flowers turning their faces towards the sun; no holidays at the seaside. How depressing!
Fortunately, this is not the case. The earth is part of a wonderful system that brings light into our lives.
Because the earth orbits the sun, it is called a planet. There are eight other planets that also orbit our sun. The sun and these nine planets make up our solar system. Each planet moves in its own specific orbits around the sun. Look at the following illustration of the solar system. You will see that some planets are closer to the sun, and others, which have much longer orbits, are further away from the sun. Those closest to the sun are warmer than those that are far away.
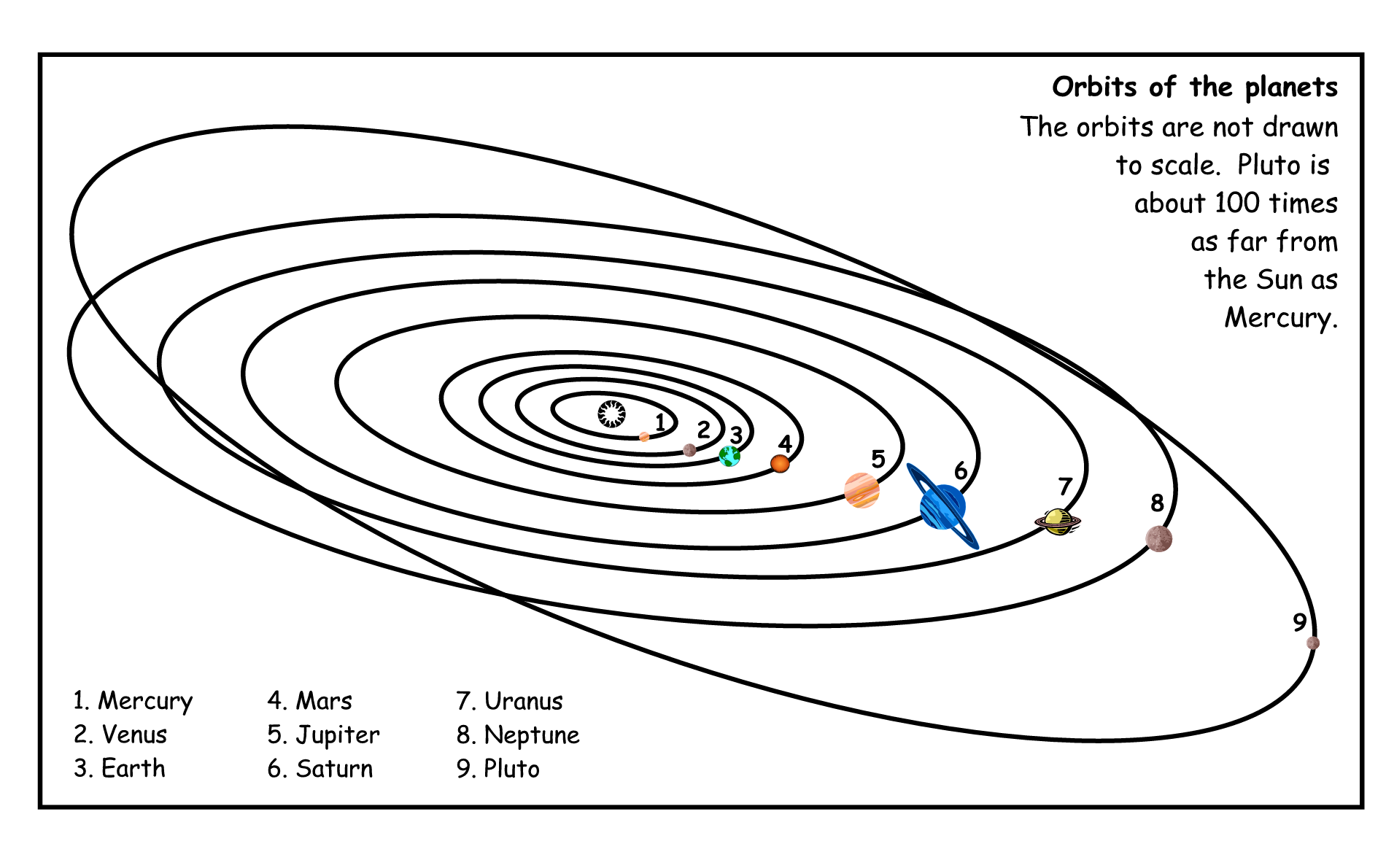
| Planet | Observation |
| Mercury | |
| Venus | |
| Earth | |
| Mars | |
| Jupiter | |
| Saturn | |
| Uranus | |
| Neptune | |
| Pluto |
3. Choose a classmate and ask him/her the following questions. He/she must answer in full sentences, starting with the words given below.
(a) Which of the planets do you find most interesting?
I find ………………………………………………………………………
(b) What do you like about it?
I like…………………………………………………………………
(c) What would you do if you were given the chance some day to visit one of the planets?
I would ………………………………………………………………
(d) Do you know any other names for Venus?
Yes, …………………………………………………………………
(e) What are they?
Venus is ……………………………………………………………
1. Read the following nursery rhyme:
Twinkle twinkle little star
How I wonder what you are
Up above the world so high
Like a diamond in the sky
Twinkle twinkle little star
How I wonder what you are
(a) See if you can find a word with the same meaning as “twinkle”, and read the rhyme again, using this word in the place of “twinkle”.
The word is …………………………………………………
(b) How does it sound to you? Which do you prefer: your word, or the one in the poem?
I prefer ………………………………………………………
(c) Look carefully at the way in which this rhyme was made (its structure). Now complete the following sentences:
The first two lines are …………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………
The words that rhyme are…………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………
(d) Does “twinkle twinkle” sound better than just “twinkle” (once)?
…………………………………………………………………………..
(e) If your answer to the previous question was “Yes”, can you try to explain why it is better?
………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………….
(f) Can you find a comparison (also called a simile) in the rhyme? If so, write it down.
…………………………………………………………………………..
(g) Do you think it is an effective comparison in the rhyme? If so, why?
……………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………
(h) Try to write your own rhyme in the same style as this one (6 lines, same kind of rhyme scheme, one comparison, repetition, etc). Your topic must be related in some way to the general topic of this module.
…………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………….
(i) Ask your teacher to sing or play the rhyme to you. It is usually sung to very young children or infants as a lullaby. Try to sing along.
(j) Do you know any other lullabies? See how many you know, and share them with your classmates. You can sing them in any other language; not only in English. Listen to each other’s songs, and talk about them – how they differ, what the words mean, and so on. How many of you know the same songs? This is a good time to learn some new lullabies in different languages.
The learner will be able to communicate effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
We know this when the learner:
2.3.3 describes people, objects and simple processes.
LEARNING OUTCOME 3: READING AND VIEWING
The learner will be able to read and view for information and enjoyment, and to respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.
We know this when the learner:
3.2 understands, in a very simple way, some elements of poetry:
3.2.1 rhyme;
3.2.2 words which begin with the same sound (e.g. “Naughty Nomsa never listens.”);
3.2.3 words that imitate their sound (e.g. swish, swish);
3.2.4 differences in the way languages represents these sounds (e.g. “cluck cluck” and “kri kri”.
LEARNING OUTCOME 5: THINKING AND REASONING
The learner will able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
We know this when the learner:
5.4 transfers information from one mode to another (e.g. chart to text):
5.4.3 uses information from a chart, graph or diagram to write a short text.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?