| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
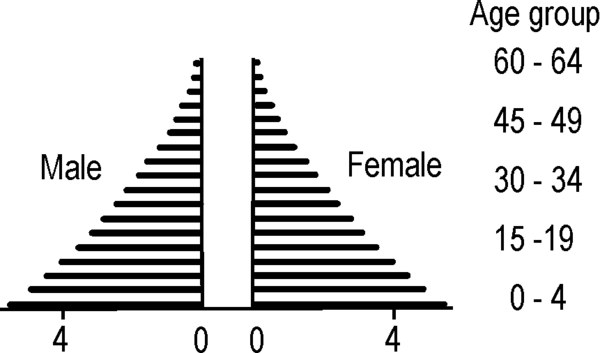
Figure 1 above represents a very “young” population. The vast majority are under 20 years of age, which also means that the population growth will be very high.
2. The population distribution across the globe
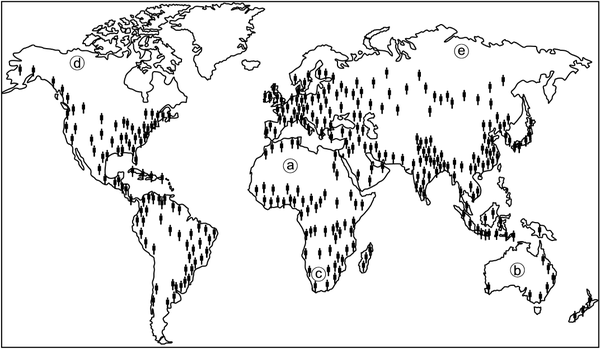
a) Why is the population so sparse at a , b and c ?
b) Why would the population at d and e be equally sparse?
c) Does the Amazon River in Brazil have anything to do with the population density in that country? (Explain)
d) Explain the reason for the densely populated area in the north-eastern corner of Africa.
e) Would you say that the whole of Australia has become urbanised?
The world population is not distributed evenly across the globe – in some parts the population is very high, while in others it is rather low. The reasons for this may vary from region to region, and from country to country. In the same way the population structures (with regard to e.g. age distribution) might also vary – one area would have an “old” population, while another would be regarded as “young”. Also, these characteristics of the population do not remain static – some regions could experience depopulation, while others might experience rapid urbanisation. In the same way a population could within 50 years possibly change from “young” to “old”. Could you think of any nearby town or village having either a “young” or “old” population? Why would that be? Has it already changed, or is it likely to change in any way, and why?
3. Population structures
This young population as depicted by means of the population pyramid in figure 1 on p. 5 was that of England and Wales in 1881. Fifty years later the picture looked quite different, and after a further fifty years it showed even more change. This type of change is called demographic development.
Important features of a population represented by means of a typical pyramid (having a broad basis), are (a) a high birth rate, (b) a high death rate, (c) short life expectancy.
The increase in the population of any group (a country or community) is calculated by means of the following formula:
Pg is the P opulation g rowth
B is the B irth rate
M is the D eath rate
immigrants are added
emigrants are deducted
a) Is it possible that the Pg does not show an increase , but a decrease ? Motivate your answer.
3.1 Is the new baby going to be a male or female ( a boy or a girl)?
We take it for granted that an equal number of boys and girls are born in a big community or country . This means that in big, co-educational schools, one would usually find a more or less equal number of girls and boys. A drawing of the school’s “population pyramid” (watch out: it will not be shaped like a pyramid, but could you explain why?) would therefore be symmetrical .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Geography grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?