| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
KHÁI NIỆM CHUNG VỀ MẠCH TỪ
Các thiết bị điện như rơle, công tắc tơ, khởi động từ, áp tô mát,...đều có bộ phận làm nhiệm vụ biến đổi từ điện năng ra cơ năng. Bộ phận này gồm có cuộn dây và mạch từ gọi chung là cơ cấu điện từ, chia làm hai loại xoay chiều và một chiều. Để nắm được những quy luật điện từ ta xét mạch từ và phương pháp tính toán mạch từ.

Mạch từ được chia làm các phần:
- Thân mạch từ.
- Nắp mạch từ.
- Khe hở không khí chính và khe hở phụ p.
- Khi cho dòng điện chạy vào cuộn dây thì trong cuộn dây có từ thông đi qua, từ thông này cũng chia làm ba phần :
a) Từ thông chính là thành phần qua khe hở không khí gọi là từ thông làm việc lv.
b) Từ thông tả̉n t là thành phần đi ra ngoài khe hở không khí xung quanh
c) Từ thông rò r là thành phần không đi qua khe hở không khí chính mà khép kín trong không gian giữa lõi và thân mạch từ.
Tính toán mạch từ thực chất là giải hai bài toán:
F = IW loại này gặp khi thiết kế một cơ cấu điện từ mới.
b) Bài toán nghịch : biết sức từ động F = IW cần tìm từ thông (gặp khi kiểm nghiệm các cơ cấu điện từ có sẵn).
Để giải quyết được hai bài toán trên cần phải dựa vào các cơ sở lí thuyết sau:
- Biết đường cong từ hóa của vật liệu sắt từ.
- Nắm vững các định luật cơ bản về mạch từ.
- Biết được từ dẫn khe hở.
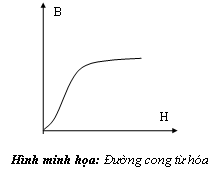
b) Các định luật cơ bản mạch từ
+ Định toàn dòng điện
+ Định luật Ohm trong mạch từ:
+Định luật Kiếc Khốp 1 cho mạch từ :
+Định luật Kiếc Khốp 2 cho mạch từ: (tổng đại số độ sụt từ áp trên một mạch từ kín bằng tổng đại số các sức từ động tác dụng trong mạch từ đó).
c) Từ dẫn của khe hở
Vì mạch từ có độ từ thẩm (hệ số dẫn từ) lớn hơn không khí nhiều nên từ trở toàn bộ mạch từ hầu như chỉ phụ thuộc vào từ trở khe hở không khí. Trong tính toán thường dùng từ dẫn . Tương tự như mạch điện thì trong mạch từ dẫn G tỉ lệ thuận với tiết diện mạch từ, tỉ lệ nghịch với chiều dài khe hở không khí.
Có : với:
+ :từ dẫn khe hơ ̉ không khí.
+ : hệ số từ thẩm không khí.
+ [cm]: chiều dài khe hở.
+S [ cm2]: diện tích từ thông đi qua ( tiết diện).
Công thức này dùng trên cơ sở giả thiết : từ thông qua khe hở không khí phân bố đều đặn ( các đường sức từ song song với nhau), công thức chỉ đúng khi khe hở rất bé, (khe hở lớn thì càng ra mép càng không song song). Thực tế tính từ dẫn rất phức tạp, tùy yêu cầu chính xác mà có các phương pháp tính từ dẫn khác nhau.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Giáo trình thiết bị điện' conversation and receive update notifications?