| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Each YD, , such that corresponds to two SYD's: and . These two SYD's are given and . Thus we define
Each YD, , such that but has only one corresponding SYD: . Thus, we define
Similarly, we define
Also,
The first method we devised for sampling SYD's according to the probability distribution in formula [link] was simply to “triple” the young diagrams , and , and then remove the boxes in either or based on the conditional probabilities based on . Unfortunately, we found a simple counterexample that proved that this method does not work because the partial ordering of YD's is not preserved due to the monotonicity of our probability distribution on YD's as stated in "The Probability Distribution on the YD's" breaking in some places (see [link] for the counterexample).
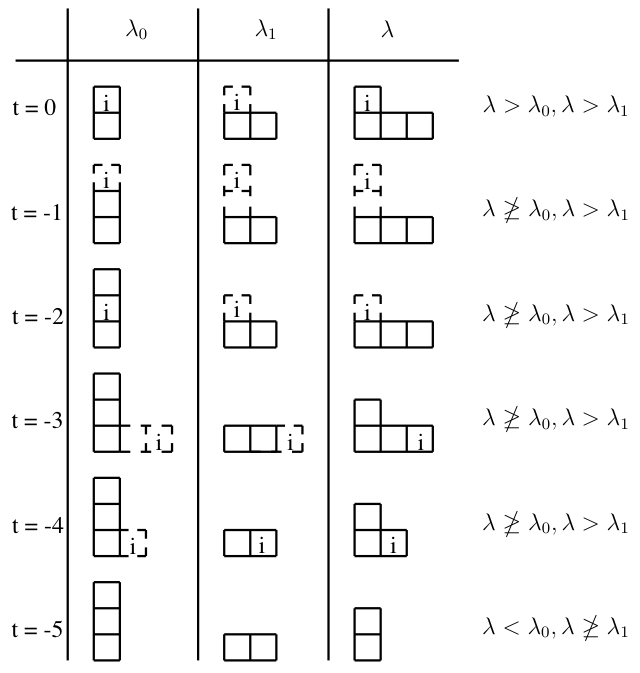
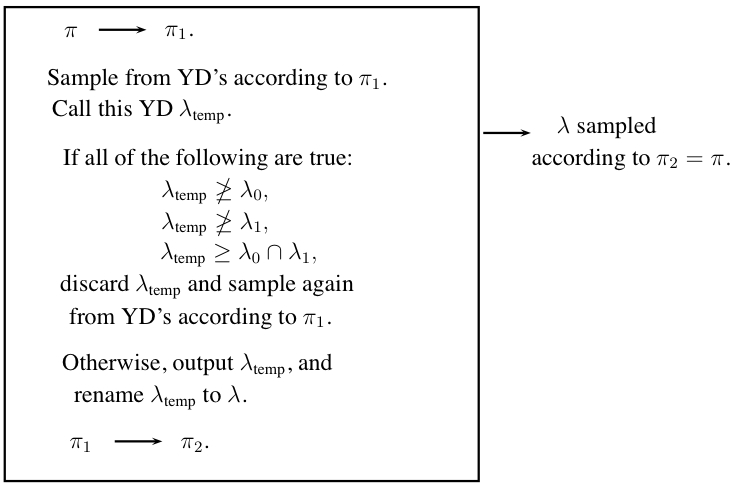
Since the method of tripling from the past did not work, we devised another method which we call the black box approach. With this approach, we change the probability distribution by giving positive probability proportional to to young diagrams such that and . Then we sample according to this new distribution, and if the sampled YD satisfies all of the following:
discard and sample another YD according to the new distribution until the sampled YD satisfies: at least one of . When we sample a such that at least one of , then we output and rename it . It is easily seen that the output, , has been sampled according to the probability distribution stated in "The Probability Distribution on the YD's" . See [link] for a schematic of the Black Box Approach.
Theorem: The following values of X give a monotonic distribution for sampling:
We will begin by numbering the possible categories of and as follows:
We will label first, second, third, and fourth. For example, 1234 represents the situation where belongs to category 1, belongs to category 2, belongs to category 3, and belongs to category 4.
The possible situations for and are the following: 11, 12, 13, 14, 22, 24, 33, 34, and 44. The values of for each situation are the following:
The possible situations for and are the same situations for and . Also, the values of are the same values for for each situation.
In order to prove monotonicity, we need to show that for all possible combinations of , and , the inequality from formula [link] holds. In all of the following cases, we will prove that either the inequality holds or the combinations of , and are impossible.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'The art of the pfug' conversation and receive update notifications?