| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Quite often it is necessary to multiply one denominate number by another. To do so, we multiply the number parts together and the unit parts together. For example,
Sometimes the product of units has a physical meaning. In this section, we will examine the meaning of the products and .
The product , or, square length unit (sq length unit), can be interpreted physically as the area of a surface.
For example, 3 sq in. means that 3 squares, 1 inch on each side, can be placed precisely on some surface. (The squares may have to be cut and rearranged so they match the shape of the surface.)
We will examine the area of the following geometric figures.
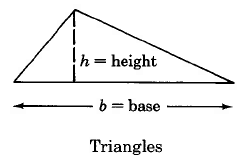
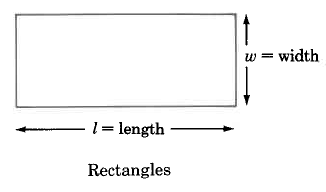
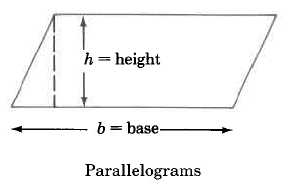
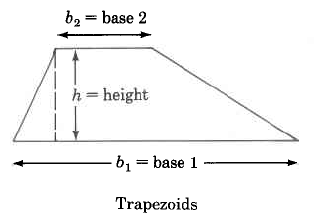
We can determine the areas of these geometric figures using the following formulas.
| Figure | Area Formula | Statement | |
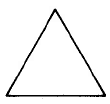 |
Triangle | Area of a triangle is one half the base times the height. | |
 |
Rectangle | Area of a rectangle is the length times the width. | |
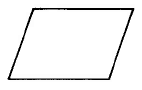 |
Parallelogram | Area of a parallelogram is base times the height. | |
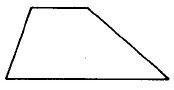 |
Trapezoid | Area of a trapezoid is one half the sum of the two bases times the height. | |
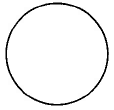 |
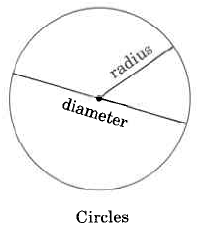
Circle | Area of a circle is times the square of the radius. |
Find the area of the triangle.
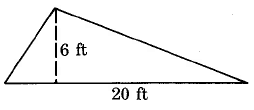
The area of this triangle is 60 sq ft, which is often written as 60 ft 2 .
Find the area of the rectangle.
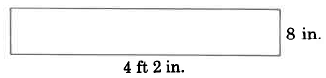
Let's first convert 4 ft 2 in. to inches. Since we wish to convert to inches, we'll use the unit fraction since it has inches in the numerator. Then,
Thus,
The area of this rectangle is 400 sq in.
Find the area of the parallelogram.
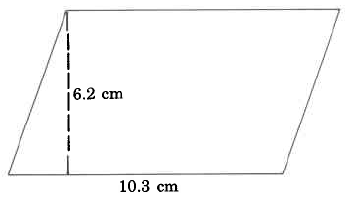
The area of this parallelogram is 63.86 sq cm.
Find the area of the trapezoid.

The area of this trapezoid is 71.545 sq mm.
Find the approximate area of the circle.
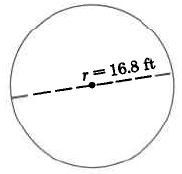
The area of this circle is approximately 886.23 sq ft.
Find the area of each of the following geometric figures.
The product , or cubic length unit (cu length unit), can be interpreted physically as the volume of a three-dimensional object.
For example, 4 cu mm means that 4 cubes, 1 mm on each side, would precisely fill some three-dimensional object. (The cubes may have to be cut and rearranged so they match the shape of the object.)
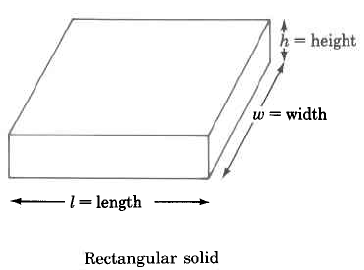
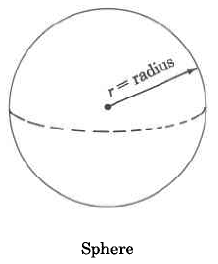
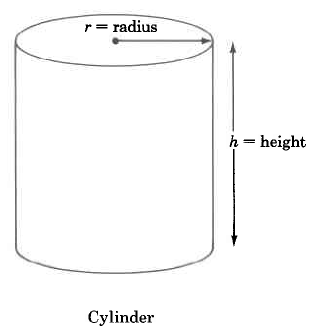
| Figure | Volume Formula | Statement | |
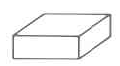 |
Rectangular solid | The volume of a rectangular solid is the length times the width times the height. | |
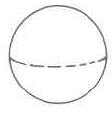 |
Sphere | The volume of a sphere is times times the cube of the radius. | |
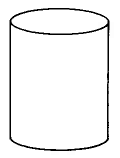 |
Cylinder | The volume of a cylinder is times the square of the radius times the height. | |
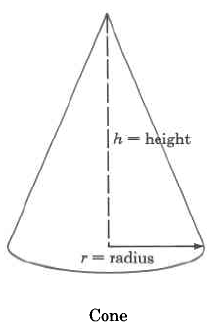
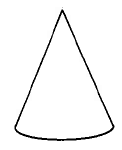 |
Cone | The volume of a cone is times times the square of the radius times the height. |
Find the volume of the rectangular solid.
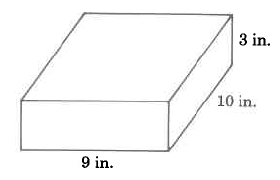
The volume of this rectangular solid is 270 cu in.
Find the approximate volume of the sphere.
The approximate volume of this sphere is 904.32 cu cm, which is often written as 904.32 cm 3 .
Find the approximate volume of the cylinder.
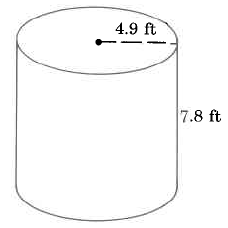
The volume of this cylinder is approximately 588.05292 cu ft. The volume is approximate because we approximated with 3.14.
Find the approximate volume of the cone. Round to two decimal places.
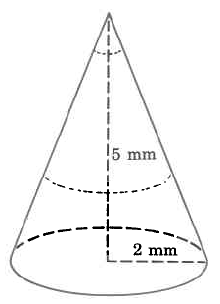
The volume of this cone is approximately 20.93 cu mm. The volume is approximate because we approximated with 3.14.
Find the volume of each geometric object. If is required, approximate it with 3.14 and find the approximate volume.
Find each indicated measurement.
Approximate area
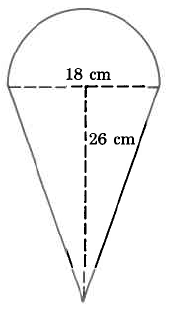
Exact area
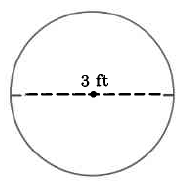
Exact area
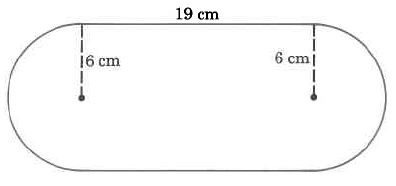
Exact volume
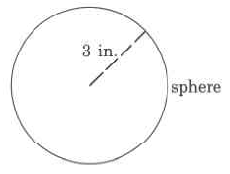
Approximate volume
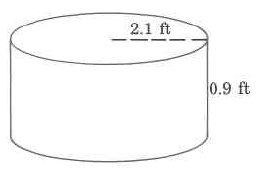
Approximate volume
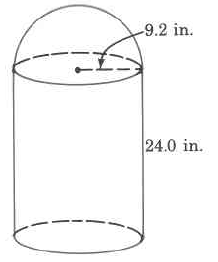
Approximate volume

( [link] ) In the number 23,426, how many hundreds are there?
4
( [link] ) List all the factors of 32.
( [link] ) Find the value of .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of mathematics' conversation and receive update notifications?