| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
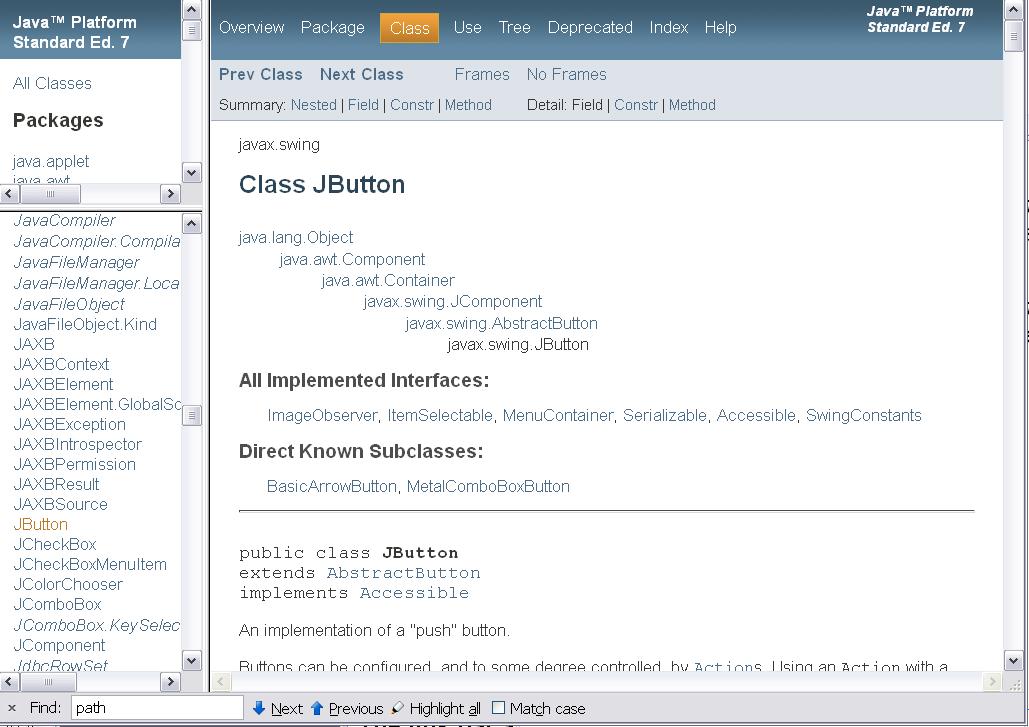
Figure 2 shows a screen shot of the browser window after selecting the class named JButton in the lower-left frame. If you pull down the thumb in the scroll bar on the right sideof the browser window, you will expose all of the information in the above list.
| Figure 2. Screen shot of the API documentation after selecting the JButton class. |
|---|
 |
The link bar at the top of the page
It can sometimes be difficult to find what you are looking for in the documentation package. Referring back to Figure 2 , you can see a link bar at the top of the page in the rightmost frame. This link bar contains the following hyperlinks:
The various pages that are displayed by selecting these links can often help you to find what you are looking for. Probably the most useful and frequentlyconsulted item in the above list is the Index.
The alphabetical index
The alphabetical index can be extremely useful if you know the full or partial spelling of what you are looking for, beginning with the firstcharacter.
For example, assume that you remember (or you can surmise from what you know about Java properties) that there is a method whose name begins with getSystemLookAndFeel , which returns the name of the LookAndFeel class that implements the native look and feel for a particular operating system. Youcan easily look this up under G in the alphabetical index.
What you will find when you look it up is a brief description of a method named getSystemLookAndFeelClassName that matches what you are looking for. The name of the method is also a hyperlink to the detailed description ofthe same method as it appears in the documentation for the class named UIManager .
The documentation for the API is created using a program named javadoc.exe that is contained in the JDK. Therefore, the API documentation for class libraries obtained from outside sources should have thesame format as that described above (assuming that the documentation was produced using javadoc.exe) .
However, the program named javadoc.exe only controls the format of the documentation. It does not produce the explanatory content. It isthe responsibility of the author of the class library to provide that content.
Typical usage of the API documentation consists of the following steps:
There are several ways to search for useful information in the Oracle documentation. There is no single approach that will serve all of your needs tofind information in the documentation. You simply need to become familiar with the different ways to search for information in the documentation and beprepared to use the approach that does the best job in each situation.
This section contains a variety of miscellaneous information.
Financial : Although the Connexions site makes it possible for you to download a PDF file for thismodule at no charge, and also makes it possible for you to purchase a pre-printed version of the PDF file, you should beaware that some of the HTML elements in this module may not translate well intoPDF.
I also want you to know that, I receive no financial compensation from the Connexions website even if you purchase the PDF version of the module.
In the past, unknown individuals have copied my modules from cnx.org, converted them to Kindle books, and placed them for sale on Amazon.com showing me as the author. Ineither receive compensation for those sales nor do I know who does receive compensation. If you purchase such a book, please beaware that it is a copy of a module that is freely available on cnx.org and that it was made and published withoutmy prior knowledge.
Affiliation : I am a professor of Computer Information Technology at Austin Community College in Austin, TX.
-end-

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Object-oriented programming (oop) with java' conversation and receive update notifications?