| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
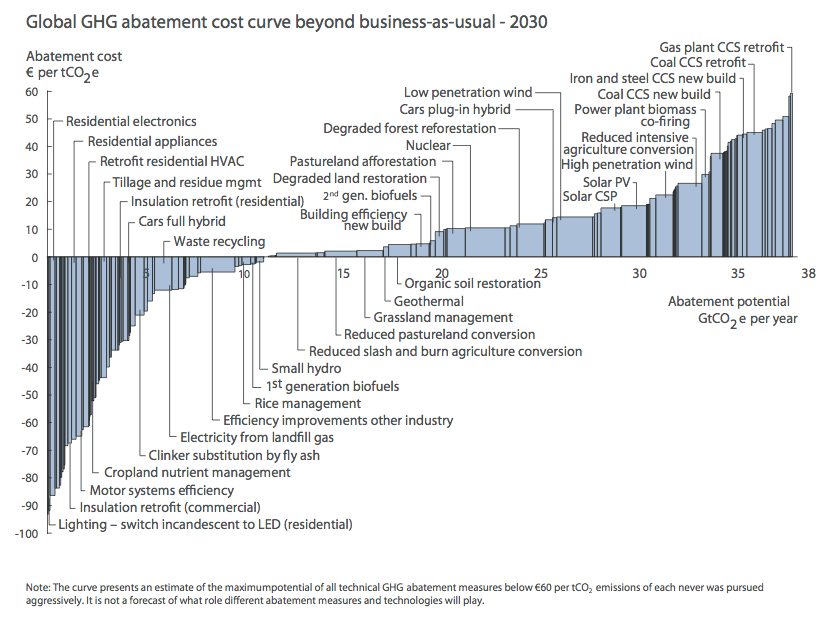
The types of technologies that fall below the line are primarily energy conservation and efficiency technologies. Energy conservation is the act of reducing energy use to avoid waste, save money, and reduce the environmental impact. In the framework of sustainable energy planning it allows the more expensive alternatives, such as renewables, to become more advanced and cost-effective, while we conserve as much as possible. Conservation has a behavioral aspect to it, such as turning off lights when not needed, lowering thermostats in the winter, or keeping the proper air pressure in a vehicle’s tires. There is a very low cost to conservation but it entails behavioral change. There are technologies such as motion detectors that can control lights or programmable thermostats that adjust temperature that can help overcome the behavioral barrier. Energy efficiency can be seen as a subset of conservation as it is really about using technological advancements to make more efficient energy-consuming equipment.
In the United States we use twice as much energy per dollar of GDP as most other industrialized nations (see Figure Energy Demand and GDP Per Capita (1980-2004) ). There are many reasons for this. One reason is that we use less efficient vehicles and use proportionally more energy to heat and cool buildings, behaviors that could be modified to be more efficient.
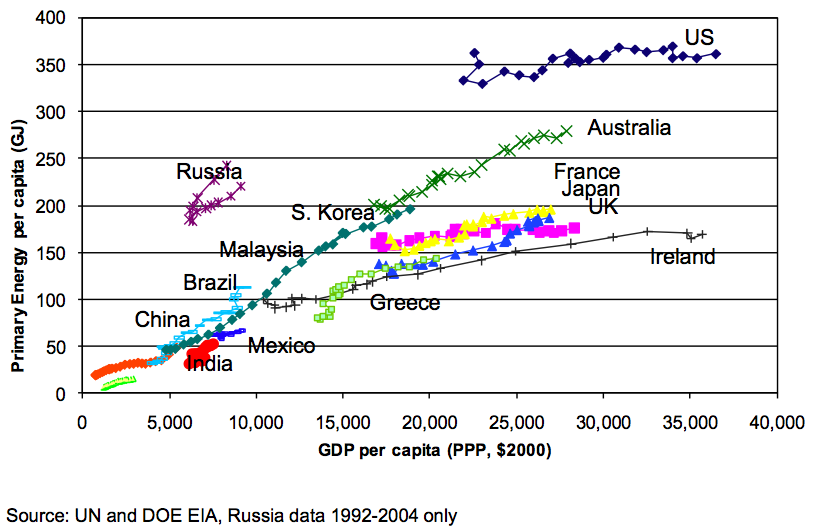
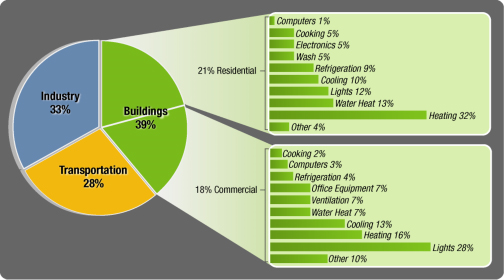
Another reason that the United States uses so much more energy than other industrialized countries has to do with heating, cooling, and illuminating buildings. Buildings account for about 40 percent of total energy consumption in the United States (costing $350 billion per year) and greenhouse gas emissions (see Figure U.S. Energy Consumption by Source ). Energy use in buildings is primarily for heating, cooling, and illumination, with significant differences between commercial and residential buildings. The rest of the energy use is for equipment such as office equipment, electronics, refrigeration, cooking, and washing. There are many ways to save energy in existing buildings and most of them have a good financial benefit of saving money on the energy costs, i.e. they have a short term financial payback, or return on investment (ROI).
The most prevalent message in energy efficiency is "change the light bulbs." Replacing traditional incandescent light bulbs with compact fluorescent light bulbs can save energy. The light bulb had not evolved much since Thomas Edison perfected it in 1879. Over the last few years there have been major initiatives across the United States to replace inefficient incandescent light bulbs with compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) that can reduce energy use by 75 percent. The light bulbs also last 10 times as long, reducing waste and maintenance costs. In commercial buildings more efficient fluorescent light bulbs (T-8s) and ballasts are replacing the older T-12s. In 2002, the U.S. Department of Energy required that T-12 ballasts no longer be manufactured, ending a five year phase out of this technology.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?