| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Up ... up ... up...
I go
looking down on Earth
below
the moon I pass
with daring swing
and over there ...
a shiny thing ...
a star!
and many millions more
I dodge the planets one by one
here’s Venus
oh it’s really fun!
and Pluto there
the smallest one
I glide my rocket
down a sunbeam
and land in my bed ...
it was just a dream
A.V

It is every child’s dream to travel into space but few of us have the wonderful opportunity that Mark Shuttleworth had when he was able to go into outer space in 2002. But we can find out much about space by using a telescope.
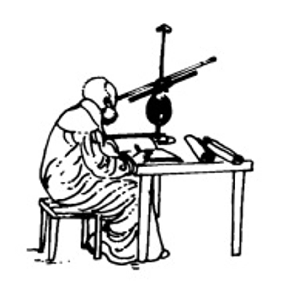
Here are some ideas:
We live below a very deep layer of air that we call the atmosphere. The atmosphere provides us with oxygen to breathe; it keeps us warm and protects us from the rays of the sun. If we travel away from the earth through the earth’s atmosphere, the air becomes thinner and thinner and it becomes very difficult to breathe. At a height of about 10 km it is not possible to breathe without extra oxygen. At a height of 160 km above the earth’s surface there is hardly any air at all. Here we really are on our way into space!
In space there is no atmosphere. Sound does not travel and weather conditions, as we know them on earth, are unknown. Space begins where earth’s atmosphere ends. But we do not know where space ends. Spacecraft have already travelled from earth and deep into the universe, but have not yet reached any of the stars that are very far away. These stars are millions of kilometres away.
LEARNING OUTCOME 1: SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATIONSThe learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
Assessment Standard
We know this when the learner
1.3 evaluates data and provides feedback on observations.
LEARNING OUTCOME 3: SCIENCE, SOCIETY AND THE ENVIRONMENTThe learner will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the interrelationships between science and technology, society and the environment.
Assessment Standard
We know this when the learner
3.1 understands science and technology in the context of history and personal knowledge.
Read the poem to the class and let them draw a picture. Let them look for more poems or reports on space that they can read to the class.
Make your own telescope from waste material. You can get ideas in various books

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?