| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The slightly granular material among the cells in [link] are cytoplasmic fragments of cells formed in the bone marrow. These are called platelets or thrombocytes. Platelets are a key player in the formation of blood clots, which are important in keeping your blood in your body when you get cut or scraped.
There are three types of muscle in animal bodies: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac. They differ by the presence or absence of striations or bands, the number and location of nuclei, whether they are voluntarily or involuntarily controlled, and their location within the body. [link] summarizes these differences. You will learn more about these cells and their functions later in this unit
| Types of Muscles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Muscle | Striations | Nuclei | Control | Location |
| smooth | no | single, in center | involuntary | visceral organs |
| skeletal | yes | many, at periphery | voluntary | skeletal muscles |
| cardiac | yes | single, in center | involuntary | heart |
Smooth muscle does not have striations in its cells. It has a single, centrally located nucleus, as shown in [link] . Constriction of smooth muscle occurs under involuntary, autonomic nervous control and in response to local conditions in the tissues. Smooth muscle tissue is also called non-striated as it lacks the banded appearance of skeletal and cardiac muscle. The walls of blood vessels, the tubes of the digestive system, and the tubes of the reproductive systems are composed of mostly smooth muscle.
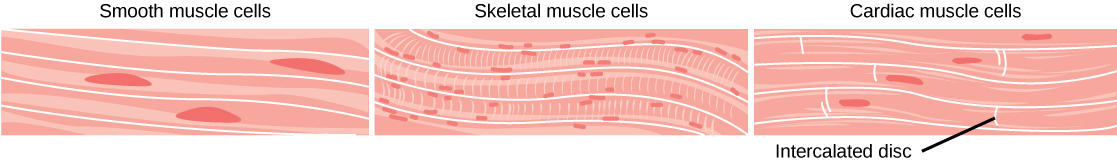
Skeletal muscle has striations across its cells caused by the arrangement of the contractile proteins actin and myosin. These muscle cells are relatively long and have multiple nuclei along the edge of the cell. Skeletal muscle is under voluntary, somatic nervous system control and is found in the muscles that move bones. [link] illustrates the histology of skeletal muscle.
Cardiac muscle, shown in [link] , is found only in the heart. Like skeletal muscle, it has cross striations in its cells, but cardiac muscle has a single, centrally located nucleus. Cardiac muscle is not under voluntary control but can be influenced by the autonomic nervous system to speed up or slow down. A structure found only in cardiac muscle cells is is at the end of the cell where it abuts the next cardiac cell in the row. This structure is called an intercalated disc: it assists in passing electrical impulses efficiently from one cell to the next, and maintains the strong synchrony needed to make the heart chambers work together efficiently.
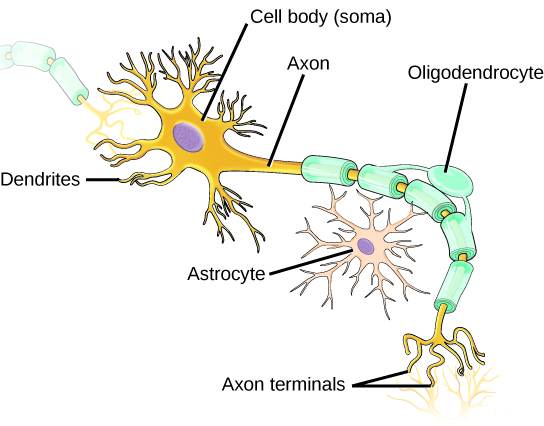
Nervous tissues are made of cells specialized to receive and transmit electrical impulses from specific areas of the body and to send them to specific locations in the body. The main cell of the nervous system is the neuron, illustrated in [link] . The large structure with a central nucleus is the cell body of the neuron. Projections from the cell body are either dendrites specialized in receiving input or a single axon specialized in transmitting impulses. Some glial cells are also shown. Astrocytes regulate the chemical environment of the nerve cell, and oligodendrocytes insulate the axon so the electrical nerve impulse is transferred more efficiently. Other glial cells that are not shown support the nutritional and waste requirements of the neuron. Some of the glial cells are phagocytic and remove debris or damaged cells from the tissue. A nerve in your body consists of neurons and glial cells.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?