| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When polar covalent bonds containing a hydrogen atom form, the hydrogen atom in that bond has a slightly positive charge. This is because the shared electron is pulled more strongly toward the other element and away from the hydrogen nucleus. Because the hydrogen atom is slightly positive (δ+), it will be attracted to neighboring negative partial charges (δ–). When this happens, a weak interaction occurs between the δ+ charge of the hydrogen atom of one molecule and the δ– charge of the other molecule. This interaction is called a hydrogen bond . This type of bond is common; for example, the liquid nature of water is caused by the hydrogen bonds between water molecules ( [link] ). Hydrogen bonds give water the unique properties that sustain life. If it were not for hydrogen bonding, water would be a gas rather than a liquid at room temperature.
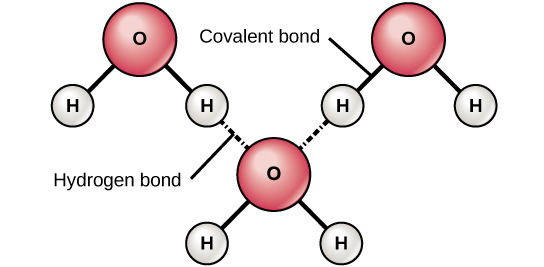
Hydrogen bonds can form between different molecules and they do not always have to include a water molecule. Hydrogen atoms in polar bonds within any molecule can form bonds with other adjacent molecules. For example, hydrogen bonds hold together two long strands of DNA to give the DNA molecule its characteristic double-stranded structure. Hydrogen bonds are also responsible for some of the three-dimensional structure of proteins.
Like hydrogen bonds, van der Waals interactions are weak attractions or interactions between molecules. They occur between polar, covalently bound, atoms in different molecules. Some of these weak attractions are caused by temporary partial charges formed when electrons move around a nucleus. These weak interactions between molecules are important in biological systems.
MRI imaging works by subjecting hydrogen nuclei, which are abundant in the water in soft tissues, to fluctuating magnetic fields, which cause them to emit their own magnetic field. This signal is then read by sensors in the machine and interpreted by a computer to form a detailed image.
Some radiography technologists and technicians specialize in computed tomography, MRI, and mammography. They produce films or images of the body that help medical professionals examine and diagnose. Radiologists work directly with patients, explaining machinery, preparing them for exams, and ensuring that their body or body parts are positioned correctly to produce the needed images. Physicians or radiologists then analyze the test results.
Radiography technicians can work in hospitals, doctors’ offices, or specialized imaging centers. Training to become a radiography technician happens at hospitals, colleges, and universities that offer certificates, associate’s degrees, or bachelor’s degrees in radiography.
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. It is made up of atoms of different elements. All of the 92 elements that occur naturally have unique qualities that allow them to combine in various ways to create compounds or molecules. Atoms, which consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons, are the smallest units of an element that retain all of the properties of that element. Electrons can be donated or shared between atoms to create bonds, including ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds, as well as van der Waals interactions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry (gpc)' conversation and receive update notifications?