This module is from Elementary Algebra by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr.
This chapter contains many examples of arithmetic techniques that are used directly or indirectly in algebra. Since the chapter is intended as a review, the problem-solving techniques are presented without being developed. Therefore, no work space is provided, nor does the chapter contain all of the pedagogical features of the text. As a review, this chapter can be assigned at the discretion of the instructor and can also be a valuable reference tool for the student.
Overview
- Multiples
- Common Multiples
- The Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- Finding The Least Common Multiple
Multiples
Multiples
When a whole number is multiplied by other whole numbers, with the exception of Multiples zero, the resulting products are called
multiples of the given whole number.
|
Multiples of 2 |
|
Multiples of 3 |
|
Multiples of 8 |
|
Multiples of 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| … |
|
… |
|
… |
|
… |
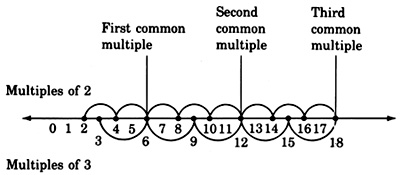
Common multiples
There will be times when we are given two or more whole numbers and we will need to know if there are any multiples that are common to each of them. If there are, we will need to know what they are. For example, some of the multiples that are common to 2 and 3 are 6, 12, and 18.
Sample set a
The least common multiple (lcm)
Notice that in our number line visualization of common multiples (above) the first common multiple is also the smallest, or
least common multiple, abbreviated by
LCM.
Least common multiple
The
least common multiple, LCM, of two or more whole numbers is the smallest whole number that each of the given numbers will divide into without a remainder.
Finding the least common multiple
Finding the lcm
To find the LCM of two or more numbers,
- Write the prime factorization of each number, using exponents on repeated factors.
- Write each base that appears in each of the prime factorizations.
- To each base, attach the largest exponent that appears on it in the prime factorizations.
- The LCM is the product of the numbers found in step 3.
Sample set b
Find the LCM of the following number.
9 and 12
-
- The bases that appear in the prime factorizations are 2 and 3.
- The largest exponents appearing on 2 and 3 in the prime factorizations are, respectively, 2 and 2 (or
from 12, and
from 9).
- The LCM is the product of these numbers.
Thus, 36 is the smallest number that both 9 and 12 divide into without remainders.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
90 and 630
-
- The bases that appear in the prime factorizations are 2, 3, 5, and 7.
- The largest exponents that appear on 2, 3, 5, and 7 are, respectively, 1, 2, 1, and 1.
- The LCM is the product of these numbers.
Thus, 630 is the smallest number that both 90 and 630 divide into with no remainders.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
33, 110, and 484
-
- The bases that appear in the prime factorizations are 2, 3, 5, and 11.
- The largest exponents that appear on 2, 3, 5, and 11 are, respectively, 2, 1, 1, and 2.
- The LCM is the product of these numbers.
Thus, 7260 is the smallest number that 33, 110, and 484 divide into without remainders.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Exercises
For the following problems, find the least common multiple of given numbers.