This module is from Elementary Algebra by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr.
Factoring is an essential skill for success in algebra and higher level mathematics courses. Therefore, we have taken great care in developing the student's understanding of the factorization process. The technique is consistently illustrated by displaying an empty set of parentheses and describing the thought process used to discover the terms that are to be placed inside the parentheses.The factoring scheme for special products is presented with both verbal and symbolic descriptions, since not all students can interpret symbolic descriptions alone. Two techniques, the standard "trial and error" method, and the "collect and discard" method (a method similar to the "ac" method), are presented for factoring trinomials with leading coefficients different from 1.
Objectives of this module: understand more clearly the factorization process, be able to determine the greatest common factor of two or more terms.
Overview
- Factoring Method
- Greatest Common Factor
Factoring method
In the last two types of problems (Sections
[link] and
[link] ), we knew one of the factors and were able to determine the other factor through division. Suppose, now, we’re given the product without any factors. Our problem is to find the factors, if possible. This procedure and the previous two procedures are based on the distributive property.
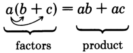
We will use the distributive property in reverse.
We notice that in the product,
is common to both terms. (In fact,
is a common factor of both terms.) Since
is common to both terms, we will
factor it out and write
Now we need to determine what to place inside the parentheses. This is the procedure of the previous section. Divide each term of the product by the known factor
Thus,
and
are the required terms of the other factor. Hence,
When factoring a monomial from a polynomial, we seek out factors that are not only common to each term of the polynomial, but factors that have these properties:
- The numerical coefficients are the largest common numerical coefficients.
- The variables possess the largest exponents common to all the variables.
Greatest common factor
A monomial factor that meets the above two requirements is called the
greatest common factor of the polynomial.
Sample set a
Factor
The greatest common factor is 3.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Factor
Notice that
is the greatest common factor.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Factor
Notice that
is the greatest common factor. Factor out
Mentally divide
into each term of the product and place the resulting quotients inside the
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Factor
We see that the greatest common factor is
Mentally dividing
into each term of the product, we get
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Practice set a
Consider this problem: factor
Surely,
We know from the very beginning of our study of algebra that letters represent single quantities. We also know that a quantity occurring within a set of parentheses is to be considered as a single quantity. Suppose that the letter
is representing the quantity
Then we have
When we observe the expression
we notice that
is common to both terms. Since it is common, we factor it out.
As usual, we determine what to place inside the parentheses by dividing each term of the product by
Thus, we get
This is a forerunner of the factoring that will be done in Section
Sample set b
Factor
Notice that
is the greatest common factor. Factor out
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Factor
.
Notice that
and
are common to both terms. Factor them out. We’ll perform this factorization by letting
Then we have
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Practice set b
Exercises
For the following problems, factor the polynomials.
Exercises for review