| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Sometimes a polynomial will not have a particular factor common to every term. However, we may still be able to produce a factored form for the polynomial.
The polynomial has no single factor that is common to every term. However, we notice that if we group together the first two terms and the second two terms, we see that each resulting binomial has a particular factor common to both terms.
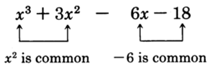
Factor out of the first two terms, and factor out of the second two terms.
Now look closely at this binomial. Each of the two terms contains the factor .
Factor out
.
is the final factorization.
We are alerted to the idea of grouping when the polynomial we are considering has either of these qualities:
When factoring by grouping, the sign of the factor we are taking out will usually (but not always) be the same as the sign of the first term in that group.
Factor .
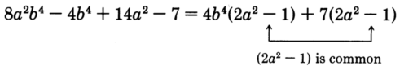
Use the grouping method to factor the following polynomials.
When factoring the polynomial
in Sample Set A, we grouped together terms1 and 2 and 3 and 4. Could we have grouped together terms1 and 3 and 2 and 4? Try this.
yes
Do we get the same result? If the results do not look precisely the same, recall the commutative property of multiplication.
For the following problems, use the grouping method to factor the polynomials. Some polynomials may not be factorable using the grouping method.
( [link] ) Simplify .
( [link] ) Find the domain of the equation .
( [link] ) Factor .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?