<para>This module is from<link document="col10614">Elementary Algebra</link>by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr.</para><para>A detailed study of arithmetic operations with rational expressions is presented in this chapter, beginning with the definition of a rational expression and then proceeding immediately to a discussion of the domain. The process of reducing a rational expression and illustrations of multiplying, dividing, adding, and subtracting rational expressions are also included. Since the operations of addition and subtraction can cause the most difficulty, they are given particular attention. We have tried to make the written explanation of the examples clearer by using a "freeze frame" approach, which walks the student through the operation step by step.</para><para>The five-step method of solving applied problems is included in this chapter to show the problem-solving approach to number problems, work problems, and geometry problems. The chapter also illustrates simplification of complex rational expressions, using the combine-divide method and the LCD-multiply-divide method.</para><para>Objectives of this module: be able to divide a polynomial by a monomial, understand the process and be able to divide a polynomial by a polynomial.</para>
Overview
- Dividing a Polynomial by a Monomial
- The Process of Division
- Review of Subtraction of Polynomials
- Dividing a Polynomial by a Polynomial
Dividing a polynomial by a monomial
The following examples illustrate how to divide a polynomial by a monomial. The division process is quite simple and is based on addition of rational expressions.
Turning this equation around we get
Now we simply divide
into
, and
into
. This should suggest a rule.
Dividing a polynomial by a monomial
To divide a polynomial by a monomial, divide every term of the polynomial by the monomial.
Sample set a
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Practice set a
Perform the following divisions.
The process of division
In Section
[link] we studied the method of reducing rational expressions. For example, we observed how to reduce an expression such as
Our method was to factor both the numerator and denominator, then divide out common factors.
When the numerator and denominator have no factors in common, the division may still occur, but the process is a little more involved than merely factoring. The method of dividing one polynomial by another is much the same as that of dividing one number by another. First, we’ll review the steps in dividing numbers.
-
We are to divide 35 by 8.
-
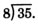 We try 4, since 32 divided by 8 is 4.
We try 4, since 32 divided by 8 is 4.
-
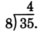 Multiply 4 and 8.
Multiply 4 and 8.
-
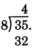 Subtract 32 from 35.
Subtract 32 from 35.
-
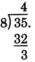 Since the remainder 3 is less than the divisor 8, we are done with the
32 division.
Since the remainder 3 is less than the divisor 8, we are done with the
32 division.
-
The quotient is expressed as a mixed number.
