| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
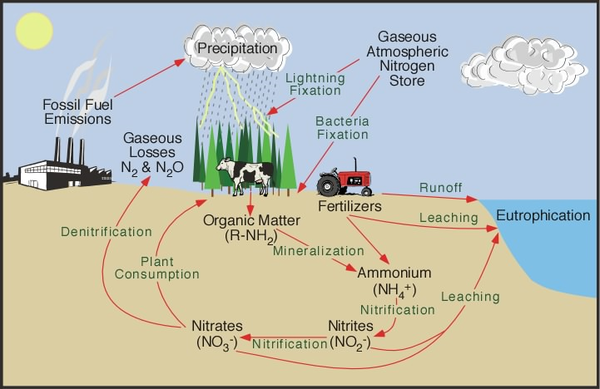
Humans are primarily dependent on the nitrogen cycle as a supporting ecosystem service for crop and forest productivity. Nitrogen fertilizers are added to enhance the growth of many crops and plantations. The enhanced use of fertilizers in agriculture was a key feature of the green revolution that boosted global crop yields in the 1970s. The industrial production of nitrogen-rich fertilizers has increased substantially over time and now matches more than half of the input to the land from biological nitrogen fixation (90 MtN each year). If the nitrogen fixation from leguminous crops (e.g. beans, alfalfa) is included, then the anthropogenic flux of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the land exceeds natural fluxes to the land. As described above, most ecosystems naturally retain and recycle almost all of their nitrogen. The relatively little nitrogen that is being gained or lost by fluxes to the atmosphere and water cycle is also nearly being balanced. When humans make large additions of nitrogen to ecosystems leakage often results, with negative environmental consequences. When the amount of nitrate in the soil exceeds plant uptake, the excess nitrate is either leached in drainage water to streams, rivers, and the ocean or denitrified by bacteria and lost to the atmosphere. One of the main gases produced by denitrifying bacteria (nitrous oxide) is an important greenhouse gas that is contributing to human-induced global warming. Other gases released to the atmosphere by denitrifying bacteria, as well as ammonia released from livestock and sewage sludge, are later deposited from the atmosphere onto ecosystems. The additional nitrogen from this deposition, along with the nitrogen leaching into waterways, causes eutrophication. Eutrophication occurs when plant growth and then decay is accelerated by an unusually high supply of nitrogen, and it has knock-on effects, including the following: certain plant species out-competing other species, leading to biodiversity loss and altered ecosystem function; algal blooms that block light and therefore kill aquatic plants in rivers, lakes, and seas; exhaustion of oxygen supplies in water caused by rapid microbial decomposition at the end of algal blooms, which kills many aquatic organisms. Excess nitrates in water supplies have also been linked to human health problems. Efforts to reduce nitrogen pollution focus on increasing the efficiency of synthetic fertilizer use, altering feeding of animals to reduce nitrogen content in their excreta, and better processing of livestock waste and sewage sludge to reduce ammonia release. At the same time, increasing demand for food production from a growing global population with a greater appetite for meat is driving greater total fertilizer use, so there is no guarantee that better practices will lead to a reduction in the overall amount of nitrogen pollution.
There is approximately 2,000 cubic kilometers of water stored in rivers around the world. Using the terms water cycle , flux and pool , describe under what conditions removing 1000 cubic kilometers per year from rivers for human use could be sustainable.
Each year, around a quarter of the carbon dioxide found in the atmosphere is turned into plant matter via photosynthesis. Does this mean that, in the absence of human activity, all carbon dioxide would be removed from the atmosphere in around four years? Explain your answer.
The water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles are all influenced by human activity. Can you describe a human activity that impacts all three cycles? In your example, which of the cycles is most significantly altered?
Le Quere, C., Raupach, M. R., Canadell, J. G., Marland, G., Bopp, L., Ciais, P., et al. (2009, December). Trends in the sources and sinks of carbon dioxide. Nature Geoscience, 2 , 831-836. doi: 10.1038/ngeo689
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005). Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis. Washington DC. Retrieved from (External Link)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?