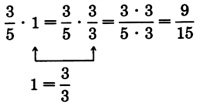This module is from Elementary Algebra by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr.
This chapter contains many examples of arithmetic techniques that are used directly or indirectly in algebra. Since the chapter is intended as a review, the problem-solving techniques are presented without being developed. Therefore, no work space is provided, nor does the chapter contain all of the pedagogical features of the text. As a review, this chapter can be assigned at the discretion of the instructor and can also be a valuable reference tool for the student.
Overview
- Equivalent Fractions
- Reducing Fractions To Lowest Terms
- Raising Fractions To Higher Terms
Equivalent fractions
Equivalent fractions
Fractions that have the same value are called
equivalent fractions.
For example,
and
represent the same part of a whole quantity and are therefore equivalent. Several more collections of equivalent fractions are listed below.
Reducing fractions to lowest terms
Reduced to lowest terms
It is often useful to convert one fraction to an equivalent fraction that has reduced values in the numerator and denominator. When a fraction is converted to an equivalent fraction that has the smallest numerator and denominator in the collection of equivalent fractions, it is said to be
reduced to lowest terms. The conversion process is called
reducing a fraction.
We can reduce a fraction to lowest terms by
- Expressing the numerator and denominator as a product of prime numbers. (Find the prime factorization of the numerator and denominator. See Section (
[link] ) for this technique.)
- Divide the numerator and denominator by all common factors. (This technique is commonly called “cancelling.”)
Sample set a
Reduce each fraction to lowest terms.
Raising a fraction to higher terms
Equally important as reducing fractions is
raising fractions to higher terms. Raising a fraction to higher terms is the process of constructing an equivalent fraction that has higher values in the numerator and denominator. The higher, equivalent fraction is constructed by multiplying the original fraction by 1.
Notice that
and
are equivalent, that is
Also,
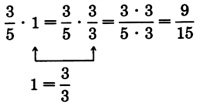
This observation helps us suggest the following method for raising a fraction to higher terms.
Raising a fraction to higher terms
A fraction can be raised to higher terms by multiplying both the numerator and denominator by the same nonzero number.
For example,
can be raised to
by multiplying both the numerator and denominator by 8, that is, multiplying by 1 in the form
How did we know to choose 8 as the proper factor? Since we wish to convert 4 to 32 by multiplying it by some number, we know that 4 must be a factor of 32. This means that 4 divides into 32. In fact,
We divided the original denominator into the new, specified denominator to obtain the proper factor for the multiplication.
Sample set b
Determine the missing numerator or denominator.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Exercises
For the following problems, reduce, if possible, each fraction lowest terms.
For the following problems, determine the missing numerator or denominator.