| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
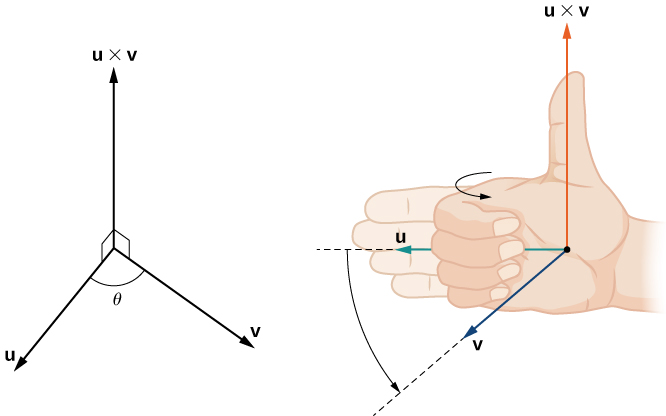
Notice what this means for the direction of If we apply the right-hand rule to we start with our fingers pointed in the direction of then curl our fingers toward the vector In this case, the thumb points in the opposite direction of (Try it!)
Let and Calculate and and graph them.
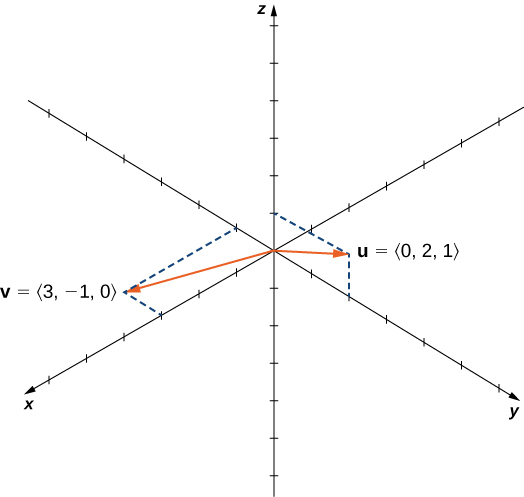
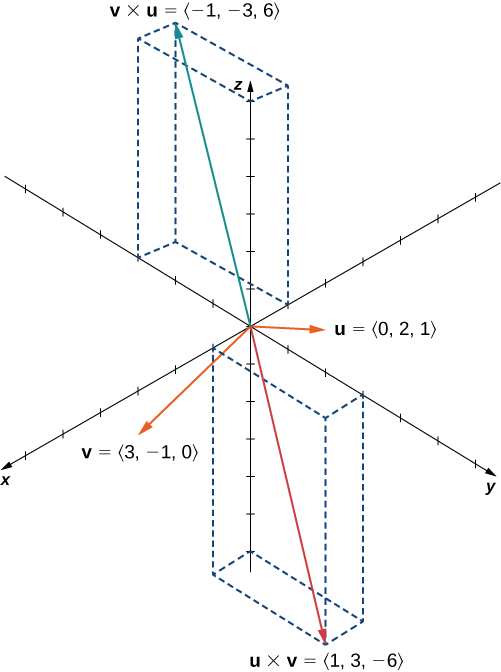
We have
We see that, in this case, ( [link] ). We prove this in general later in this section.
Suppose vectors and lie in the xy -plane (the z -component of each vector is zero). Now suppose the x - and y -components of and the y -component of are all positive, whereas the x -component of is negative. Assuming the coordinate axes are oriented in the usual positions, in which direction does point?
Up (the positive z -direction)
The cross products of the standard unit vectors and can be useful for simplifying some calculations, so let’s consider these cross products. A straightforward application of the definition shows that
(The cross product of two vectors is a vector, so each of these products results in the zero vector, not the scalar It’s up to you to verify the calculations on your own.
Furthermore, because the cross product of two vectors is orthogonal to each of these vectors, we know that the cross product of and is parallel to Similarly, the vector product of and is parallel to and the vector product of and is parallel to We can use the right-hand rule to determine the direction of each product. Then we have
These formulas come in handy later.
Find
We know that Therefore,
As we have seen, the dot product is often called the scalar product because it results in a scalar. The cross product results in a vector, so it is sometimes called the vector product . These operations are both versions of vector multiplication, but they have very different properties and applications. Let’s explore some properties of the cross product. We prove only a few of them. Proofs of the other properties are left as exercises.
Let and be vectors in space, and let be a scalar.
For property we want to show We have
Unlike most operations we’ve seen, the cross product is not commutative. This makes sense if we think about the right-hand rule.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?