| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This module describes the type of signals acted on by the Continuous Time Fourier Transform.
The Continuous-Time Fourier Transform maps infinite-length (a-periodic), continuous-time signals in to infinite-length, discrete-frequency signals in .
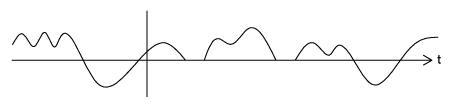
When a function repeats itself exactly after some given period, or cycle, we say it's periodic . A periodic function can be mathematically defined as:
An
aperiodic CT function
does not repeat for
any
;
Suppose we have such an aperiodic function . We can construct a periodic extension of called , where is repeated every seconds. If we take the limit as , we obtain a precise model of an aperiodic signal for which all rules that govern periodic signals can be applied, including Fourier Analysis (with an important modification). For more detail on this distinction, see the module on the Continuous Time Fourier Transform .
Any aperiodic signal can be defined by an infinite sum of periodic functions, a useful definition that makes it possible to use Fourier Analysis on it by assuming all frequencies are present in the signal.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?