| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

As a consequence of its larger size indium forms a wide range of anionic halides addition compounds with trigonal bipyramidal, square pyramidal, and octahedral coordination geometries. For example, salts of InCl 5 2- , InBr 5 2- , InF 6 3- , InCl 6 3- and InBr 6 3- have all been made. The InCl 5 2- ion has been found to be square pyramidal in the salt [NEt 4 ] 2 InCl 5 , but is trigonal bipyramidal in the acetonitrile solvate of [Ph 4 P] 2 InCl 5 . The oligomeric anionic halides In 2 X 7 - and In 2 X 9 3- (X = Cl and Br) contain binuclear anions with tetrahedral and octahedrally coordinated indium atoms, respectively ( [link] ).
Boron forms a series of low oxidation halides containing B-B bonds a formal oxidation state of +2. Passing an electric discharge through BCl 3 using mercury electrodes results in the synthesis of B 2 Cl 4 , [link] . An alternative route is by the co-condensation of copper as a reducing agent with BCl 3 , [link] .
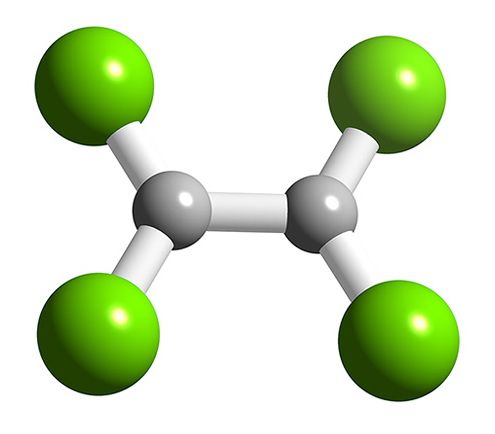
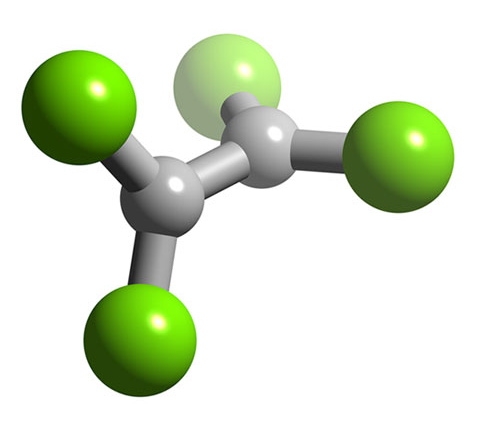
B 2 F 4 has a planar structure ( [link] ) with D2h symmetry, while B 2 Cl 4 has the same basic structure it has a staggered geometry ( [link] ). The energy for bond rotation about the B-B bond is very low (5 kJ/mol) that can be compared to ethane (12.5 kJ/mol). The bromide, B 2 Br 4 , is also observed to be staggered in the solid state. The staggered conformation is favorable on steric grounds, however, for B 2 F 4 the planar geometry is stabilized by the smaller size of the halide, and more importantly the presence of strong delocalized π-bonding.
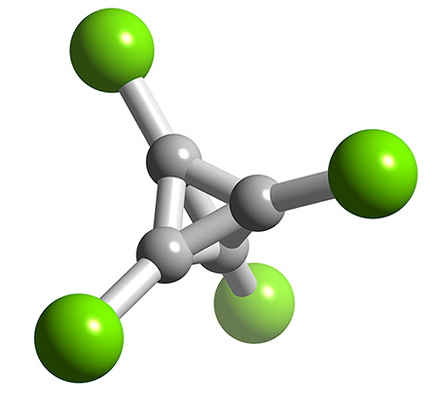
Boron forms a number of halides with cluster structures, B n Cl n where n = 4 ( [link] ), 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12. Each compound is made by the decomposition of B 2 Cl 4 . For gallium, none of the monohalides are stable at room temperature, but GaCl and GaBr have been produced in the gas form from the reaction of HX and molten gallium. The stability of thallium(I) as compared to thallium(III) results in the monohalides, TlCl, TlBr, and TlI being stable. Each compound is insoluble in water, and photosensitive.
The dihalides (MX 2 ) of gallium, indium, and thallium do not actually contain the metal in the +2 oxidation state. Instead they are actually mixed valence compound, i.e., M + [MX 4 ] - . The dihalides of gallium are unstable in the presence of water disproportionating to gallium metal and gallium(III) entities. They are soluble in aromatic solvents, where arene complexes have been isolated and the arene is η 6 -coordinated to the Ga + ion. InBr 2 and InI 2 are greenish and yellow crystalline solids, respectively, which are formulated In(I)[In(III)X 4 ]. TlCl 2 and TlBr 2 both are of similar formulations.
Ga 2 X 3 (X = Br, I) and In 2 Br 3 are formulated M(I) 2 [M(II) 2 X 6 ]. Both anions contain a M-M bond where the metal has a formal oxidation state of +2. The Ga 2 Br 6 2- anion is eclipsed like the In2Br6 2 - anion, whereas the Ga 2 I 6 2- anion is isostructural with Si 2 Cl 6 with a staggered conformation. In 2 Cl 3 is colorless and is formulated In(I) 3 [In(III)Cl 6 ].
Ga 3 Cl 7 contains the Ga 2 Cl 7 - ion, which has a structure similar to the dichromate, Cr 2 O 7 2- , ion with two tetrahedrally coordinated gallium atoms sharing a corner ( [link] ). The compound can be formulated as gallium(I) heptachlorodigallate(III), Ga(I)[Ga(III) 2 Cl 7 ].

In 4 Br 7 is light sensitive (like TlCl and TlBr) decaying to InBr 2 and In metal. It is a mixed salt containing the InBr 4 - and InBr 6 3- anions balanced by In + cations. It is formulated In(I) 5 [In(III)Br 4 ] 2 [In(III)Br 6 ]. In 5 Br 7 is a pale yellow solid formulated as In(I) 3 [In(II) 2 Br 6 ]Br. The In(II) 2 Br 6 2- anion has an eclipsed ethane like structure with an In-In bond length of 2.70 Å. In 5 Cl 9 is formulated In(I) 3 [In(III) 2 Cl 9 ], with the In 2 Cl 9 2- anion having two 6 coordinate indium atoms with 3 bridging chlorine atoms, face sharing bioctahedra. Finally, In 7 Cl 9 and In 7 Br 9 have a structure formulated as InX 6 [In(III)X 6 ]X 3 .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?