| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Essential fatty acids are fatty acids required but not synthesized by the human body. Consequently, they have to be supplemented through ingestion via the diet. Omega -3 fatty acids (like that shown in [link] ) fall into this category and are one of only two known for humans (the other being omega-6 fatty acid). These are polyunsaturated fatty acids and are called omega-3 because the third carbon from the end of the hydrocarbon chain is connected to its neighboring carbon by a double bond.
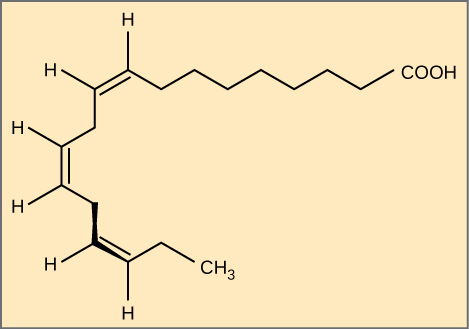
The farthest carbon away from the carboxyl group is numbered as the omega ( ω ) carbon, and if the double bond is between the third and fourth carbon from that end, it is known as an omega-3 fatty acid. Nutritionally important because the body does not make them, omega-3 fatty acids include alpha-linoleic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), all of which are polyunsaturated. Salmon, trout, and tuna are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Research indicates that omega-3 fatty acids reduce the risk of sudden death from heart attacks, reduce triglycerides in the blood, lower blood pressure, and prevent thrombosis by inhibiting blood clotting. They also reduce inflammation, and may help reduce the risk of some cancers in animals.
Like carbohydrates, fats have received a lot of bad publicity. It is true that eating an excess of fried foods and other “fatty” foods leads to weight gain. However, fats do have important functions. Many vitamins are fat soluble, and fats serve as a long-term storage form of fatty acids: a source of energy. They also provide insulation for the body. Therefore, “healthy” fats in moderate amounts should be consumed on a regular basis.
Wax covers the feathers of some aquatic birds and the leaf surfaces of some plants. Because of the hydrophobic nature of waxes, they prevent water from sticking on the surface ( [link] ). Waxes are made up of long fatty acid chains esterified to long-chain alcohols.

Phospholipids are major constituents of the plasma membrane, the outermost layer of animal cells. Like fats, they are composed of fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol or sphingosine backbone. Instead of three fatty acids attached as in triglycerides, however, there are two fatty acids forming diacylglycerol, and the third carbon of the glycerol backbone is occupied by a modified phosphate group ( [link] ). A phosphate group alone attached to a diaglycerol does not qualify as a phospholipid; it is phosphatidate (diacylglycerol 3-phosphate), the precursor of phospholipids. The phosphate group is modified by an alcohol. Phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine are two important phospholipids that are found in plasma membranes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cellular macromolecules: bis2a modules 3.0 to 3.5' conversation and receive update notifications?