| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Sunday is the first day.
of every week.
of every year.
The second day is Monday .
wake up early so
and off to school we go.
The third day is Tuesday .
porridge for me and you
and some fruit juice too.
The fourth day is Wednesday .
I’ll straighten your tie
and dish up some pie!
The fifth day is Thursday .
the sun will shine
the day is fine.
The sixth day is Friday .
there’s a cake to bake
for goodness sake!
And then its the seventh day
it’s Saturday .
no school today!
Sunday, Monday and Tuesday
Wednesday, Thursday and Friday .
S A – T U R – D A Y !
G.J.M.HIP – HIP – HOORAY!
| LO 4.2 |
Monday
Wednesday
Friday
Saterday
Tuesday
Thursday
Sunday
first
third
second
fourth
sixth
seventh
fith
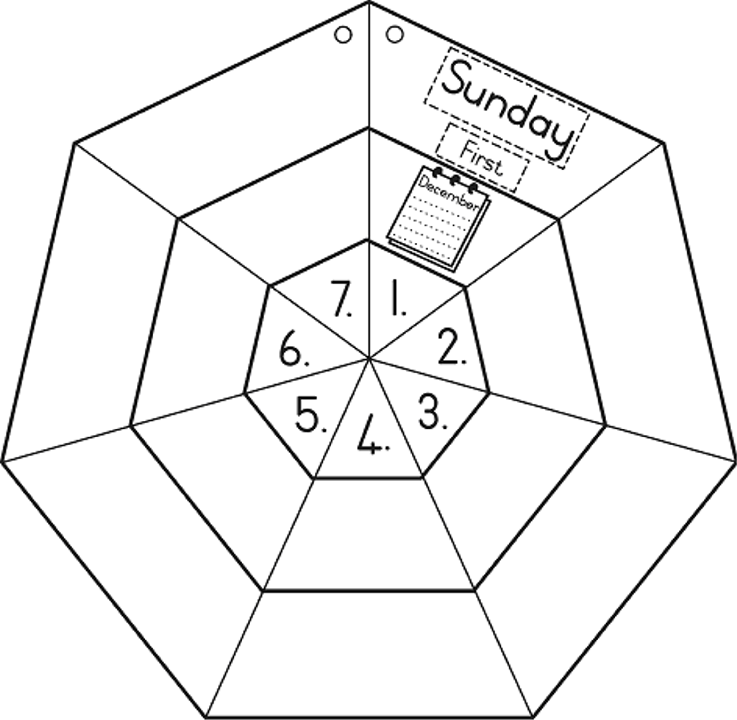
| LO 4.2 | LO 5.5 |
1. Today is.............................................................................................................
2. Tomorrow is.........................................................................................................
3. Yesterday was.......................................................................................................
4. .................................................. and ............................................. are weekend.
5. There are................................................................................... days in a week.
6. The first day of the week is............................................................................
7. The last day of the week is............................................................................
8. .......................................................................................... comes after Monday.
9. ......................................................................................... comes after Thursday.
10. ........................................................................................ comes before Monday.
11. ..................................................................................... comes before Thursday.
| LO 4.2 | LO 4.3 |
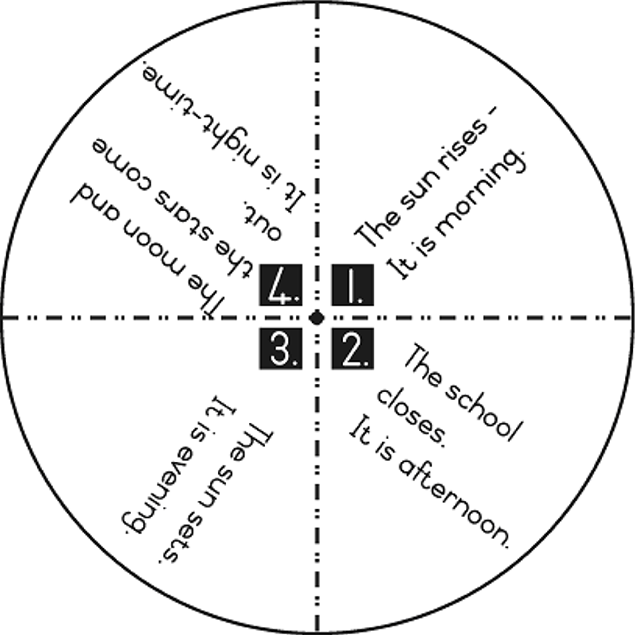
| LO 4.1 |
12 twelve
| LO 1.1 | LO 1.3 |
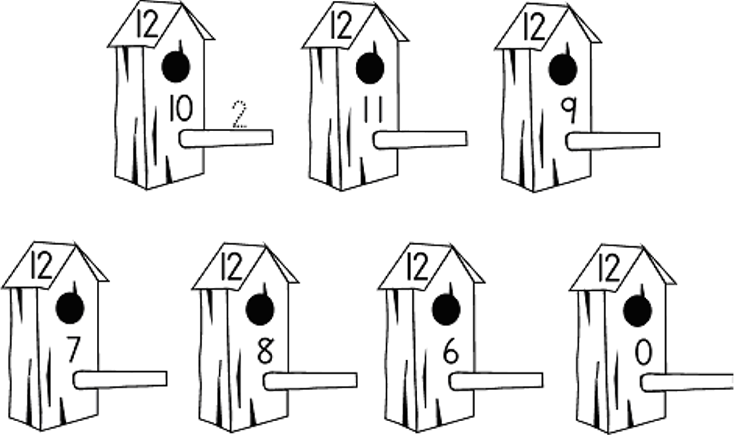
1. 12 comes after......................................................................................................
2. 12 is one more than..............................................................................................
3. 2 more than ten is.................................................................................................
4. 2 less than 12 is..................................................................................................
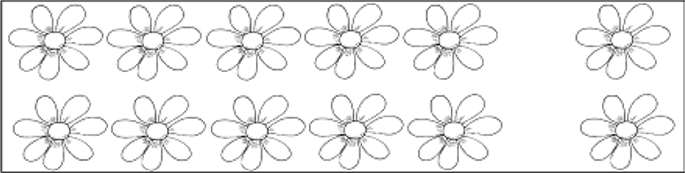
The half of 12 is..........................................................................................................
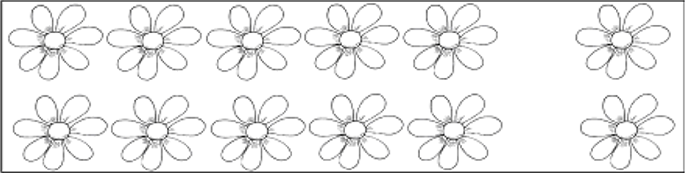
12 doubled is................................................................................................................
| LO 1.3 | LO 1.4 |
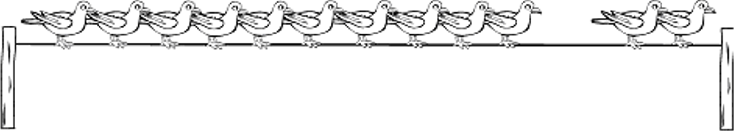
10 + 2 = 12
..........................................................
..........................................................
..........................................................
..........................................................
..........................................................
..........................................................
..........................................................
| LO 1.7 |

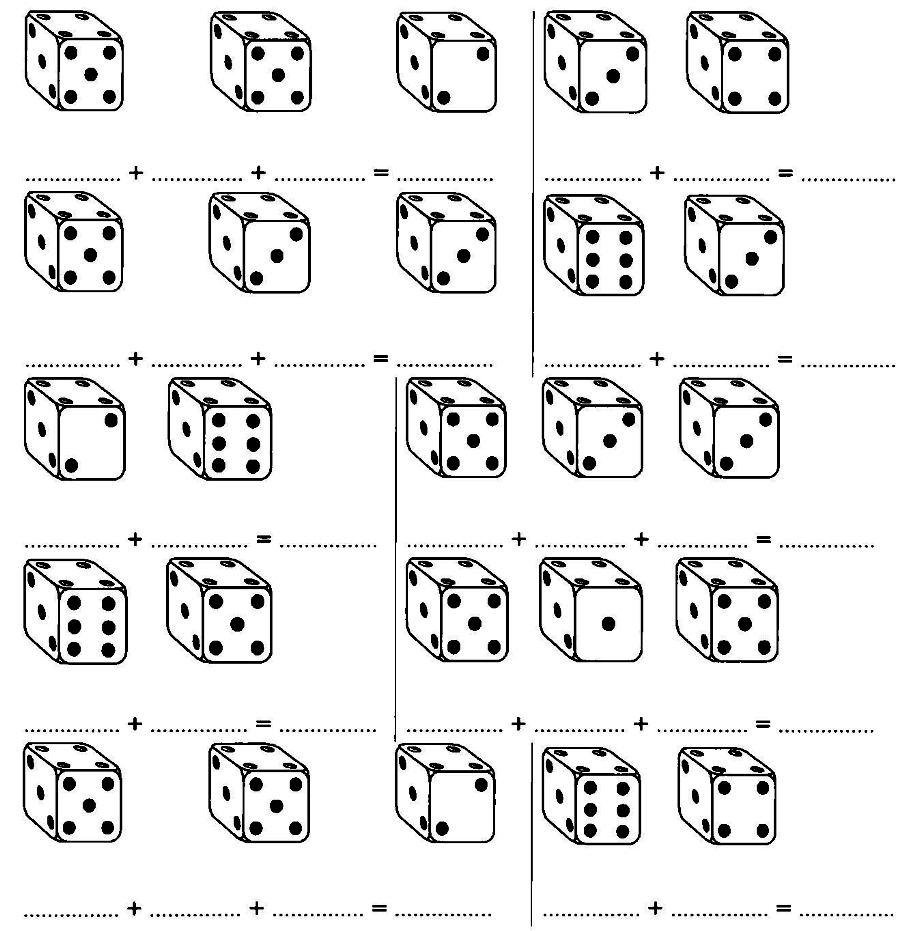
3 +3 , 6 +3 , .............., ............., ............., ............, .............., .............., ..............., 36
| LO 1.2 | LO 1.7 |
Learning Outcome 1: NUMBERS, OPERATIONS AND RELATIONSHIPS: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner counts to at least 34 everyday objects reliably;
Assessment Standard 1.2: We know this when the learner counts forward and backwards in;
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner knows and reads number symbols form 1 to at least 100 and writes number names from 1 to at least 34;
Assessment Standard 1.4: We know this when the learner orders, describes and compares whole numbers to at least 2-digit numbers;
Assessment Standard 1.7: We know this when the learner can perform calculations, using appropriate symbols, to solve problems;
Learning Outcome 4: MEASUREMENT : The learner will be able to use appropriate measuring units, instruments and formulae in a variety of contexts.
Assessment Standard 4.1: We know this when the learner describes the time of day using vocabulary such as ‘early’, late morning’, ‘afternoon’ and ‘night’;
Assessment Standard 4.2: We know this when the learner compares events in terms of the length of time they take (longer, shorter, faster, slower).
Learning Outcome 5: DATA HANDLING: The learner will be able to collect, summarise, display and critically analyse data in order to draw conclusions and make predictions, and to interpret and determine chance variation.
Assessment Standard 5.5: We know this when the learner constructs pictographs where stickers or stamps represent individual elements in a collection of objects.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 1' conversation and receive update notifications?