This module is from Fundamentals of Mathematics by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr. This module discusses how to multiply and divide signed numbers. By the end of the module students should be able to multiply and divide signed numbers and be able to multiply and divide signed numbers using a calculator.
Section overview
- Multiplication of Signed Numbers
- Division of Signed Numbers
- Calculators
Multiplication of signed numbers
Let us consider first, the product of two positive numbers. Multiply:
.
means
This suggests
that
More briefly,
Now consider the product of a positive number and a negative number. Multiply:
.
means
This suggests that
More briefly,
By the commutative property of multiplication, we get
More briefly,
The sign of the product of two negative numbers can be suggested after observing the following illustration.
Multiply -2 by, respectively, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4.
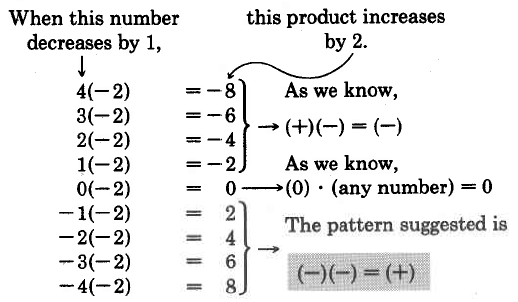
We have the following rules for multiplying signed numbers.
Rules for multiplying signed numbers
Multiplying signed numbers:
- To multiply two real numbers that have the
same sign , multiply their absolute values. The product is positive.
- To multiply two real numbers that have
opposite signs , multiply their absolute values. The product is negative.
Sample set a
Find the following products.
Multiply these absolute values.
Since the numbers have the same sign, the product is positive.
Thus,
, or
.
Multiply these absolute values.
Since the numbers have the same sign, the product is positive.
Thus,
, or
.
Multiply these absolute values.
Since the numbers have opposite signs, the product is negative.
Thus,
.
Multiply these absolute values.
Since the numbers have opposite signs, the product is negative.
Thus,
.
Practice set a
Find the following products.
Division of signed numbers
To determine the signs in a division problem, recall that
since
This suggests that
since
What is
?
suggests that
. That is,
suggests that
What is
?
suggests that
. That is,
suggests that
What is
?
suggests that
. That is,
suggests that
We have the following rules for dividing signed numbers.
Rules for dividing signed numbers
Dividing signed numbers:
- To divide two real numbers that have the
same sign , divide their absolute values. The quotient is positive.
- To divide two real numbers that have
opposite signs , divide their absolute values. The quotient is negative.
Sample set b
Find the following quotients.
Divide these absolute values.
Since the numbers have opposite signs, the quotient is negative.
Thus
.
Divide these absolute values.
Since the numbers have the same signs, the quotient is positive.
Thus,
.
Divide these absolute values.
Since the numbers have opposite signs, the quotient is negative.
Thus,
.
Practice set b
Find the following quotients.
Sample set c
Find the value of
.
Using the order of operations and what we know about signed numbers, we get,
Practice set c
Find the value of
.
Calculators
Calculators with the
 key can be used for multiplying and dividing signed numbers.
key can be used for multiplying and dividing signed numbers.
Sample set d
Use a calculator to find each quotient or product.
Since this product involves a
, we know the result should be a positive number. We'll illustrate this on the calculator.
|
|
Display Reads |
| Type |
186 |
186 |
| Press |
 |
-186 |
| Press |
× |
-186 |
| Type |
43 |
43 |
| Press |
 |
-43 |
| Press |
= |
7998 |
Thus,
.
. Round to one decimal place.
|
|
Display Reads |
| Type |
158.64 |
158.64 |
| Press |
÷ |
158.64 |
| Type |
54.3 |
54.3 |
| Press |
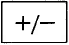 |
-54.3 |
| Press |
= |
-2.921546961 |
Rounding to one decimal place we get -2.9.
Practice set d
Use a calculator to find each value.
. Round to three decimal places.
Exercises
Find the value of each of the following. Use a calculator to check each result.
Exercises for review
(
[link] ) Use the order of operations to simplify
.
(
[link] ) Find
.
(
[link] ) Write this number in decimal form using digits: “fifty-two three-thousandths”
(
[link] ) The ratio of chlorine to water in a solution is 2 to 7. How many mL of water are in a solution that contains 15 mL of chlorine?
(
[link] ) Perform the subtraction

![]() key can be used for multiplying and dividing signed numbers.
key can be used for multiplying and dividing signed numbers.