| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Grade 3 learners continue to expand their vocabulary by listening and reading a variety of texts such as poem, stories, riddles and doing word puzzles.
These modules consolidate and revise the vocabulary and phonics introduced in Grade 2. More opportunities are given for written work producing longer texts of more varied kinds. Learners should not be afraid to make mistakes as the building of confidence and fluency should take priority above perfect written work.
Time scheduled for the modules
All learners should work through all eight modules as the phonics and spelling requirements are spread over these modules. The educator should however allow learners to complete them at their own pace namely ± two modules per term.
This story allows the learners to use their imagination when the baby Brontosaurus is found by the animals. Vocabulary is consolidated by repetitive phrases and the following phonic families are introduced; “ wh ” and silent letters such as “ b ” as in lamb, and “ k ” as in knee. Plurals are studied and homonyms sorted out.
Integration of themes
Is dependent on resources. If catastrophies occur they damage the environment.
Thunder finds himself amongst strangers. Their attitude to him is of vital importance.
Newcomers at school or in the class should be welcomed and treated with kindness and respect.
The different kinds: .........................................................................................................
When they lived: .............................................................................................................
What they ate: ..................................................................................................................
How big they were: .........................................................................................................
Why they disappeared: ....................................................................................................
| LO 1.6 | LO 2.5 | LO 2.10 | LO 3.3.1 |
one lady many ladies
one baby
many ....................................................................................
one jelly
many ....................................................................................
one fairy
many ....................................................................................
one daddy
many ....................................................................................
one mummy
many ....................................................................................
one monkey many monkeys
one donkey
many ....................................................................................
one chimney
many ....................................................................................
one key
many ....................................................................................
| LO 6.9 |
Write these sentences over, changing the underlined words into the plural (more than one).
1. I like jelly.
We .......................................................................................................................
2. The donkey eats straw.
............................................................. eat .........................................................
3. The monkey plays tricks.
............................................................play .........................................................
4. The lady buys a new dress.
................................................................................................. buy new dresses
5. The baby is crying.
................................................... are ...................................................................
6. The chimney is dirty.
..................................................... are ..................................................................
| LO 6.9 |
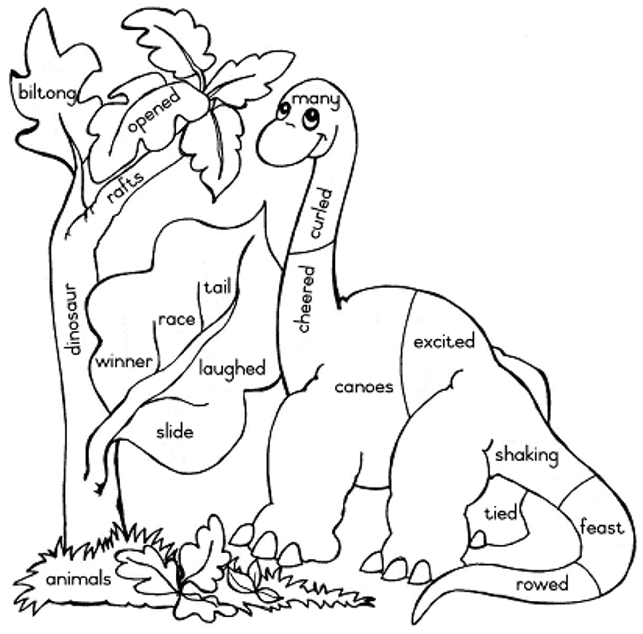
| strange | lying | curled | monster | opened |
| staring | shaking | laughed | dinosaur | tired |
| remembered | surprised | hungry | many | paths |
| swishing | tail | tallest | slide | perch |
| race | divide | rafts | canoes | winningpost |
| winner | sizes | poles | tied | excited |
| rowed | cheered | waved | huge | fruit |
| salads | biltong | ice cream | feast | paddles |
| LO 3.3.1 | LO 5.5 | LO 6.8 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner will be able to listen for information and enjoyment, and respond appropriately and critically in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.6: We know this when the learner shows respect for classmates by giving them a chance to speak.
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.5: We know this when the learner talks about a picture, photograph or object:
Assessment Standard 2.10: We know this when the learner participates in a conversation on a familiar topic:
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment, and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts;
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner recognises and makes meaning of letters and words:
3.3.1 recognises on sight an increasing number of high frequency words;
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.7: We know this when the learner keeps a personal dictionary.
Learning Outcome 6: GRAMMAR ND VOCABULARY : The learner knows and is able to use the sounds, vocabulary and grammar of the additional language.
Assessment Standard 6.8: We know this when the learner understands between 1 500 and 3 000 common spoken words in context:
Assessment Standard 6.9: We know this when the learner understands plurals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 3' conversation and receive update notifications?