| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Daar is 5 modules:
1. Getalbegrip, Optelling en Aftrekking
2. Vermenigvuldiging en Deling
3. Breuke en Desimale Breuke
4. Meting en Tyd
5. Meetkunde; Datahantering en Waarskynlikheid
4 Dit is belangrik dat opvoeders die modules in volgorde (soos hierbo genoem) sal doen, aangesien die leerders die vorige module se kennis en vaardighede benodig vir die daaropvolgende module.
3. GEWONE EN DESIMALE BREUKE (LU 1; 2 EN 5)
LEEREENHEID 1 FOKUS OP GEWONE BREUKE
LEEREENHEID 2 FOKUS OP DESIMALE BREUKE
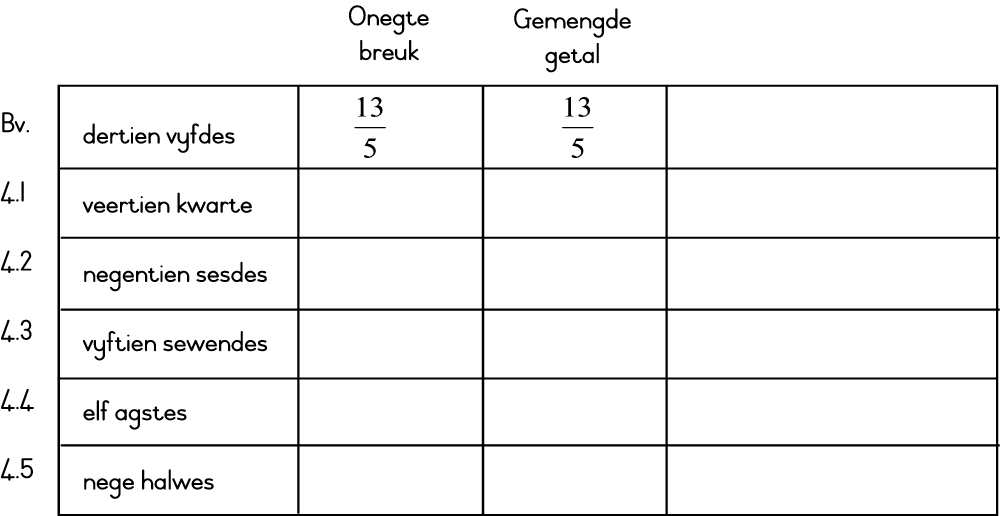
| 4. | ONEGTE BREUK | GEMENGEDE GETAL |
| 4.1 | 3 | |
| 4.2 | 3 | |
| 4.3 | 2 | |
| 4.4 | 1 | |
| 4.5 | 4 |
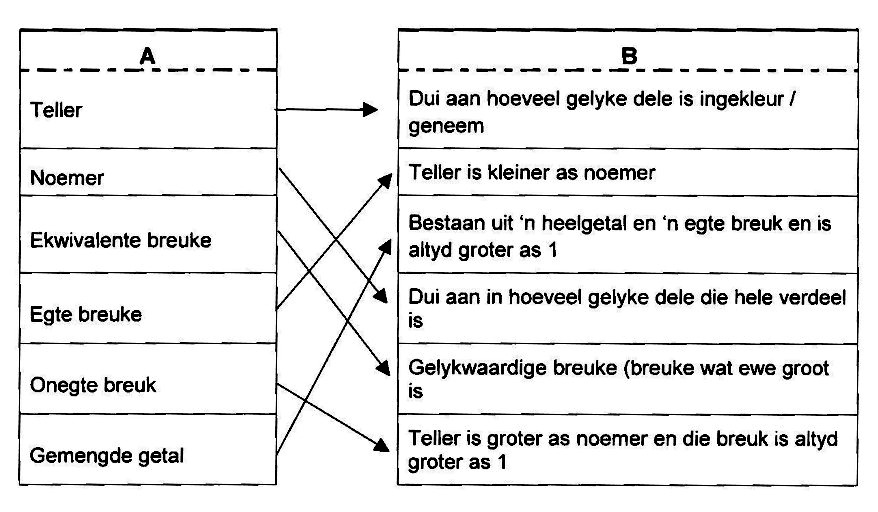
In graad 5 het ons baie met breuke gewerk. Voordat ons egter by hierdie jaar se werk kan uitkom, wil ons eers weet hoe goed jy nog onthou! Kyk of jy die woorde in kolom A met die korrekte verduideliking in kolom B kan verbind:
In graad 5 het ons baie met breuke gewerk. Voordat ons egter by hierdie jaar se werk kan uitkom, wil ons eers weet hoe goed jy nog onthou! Kyk of jy die woorde in kolom A met die korrekte verduideliking in kolom B kan verbind:
| A | B | |
| Teller | Dui aan hoeveel gelyke dele is ingekleur / geneem | |
| Noemer | Teller is kleiner as noemer | |
| Ekwivalente breuk | Bestaan uit ‘n heelgetal en ‘n egte breuk en is altyd groter as 1 | |
| Egte breuk | Dui aan in hoeveel gelyke dele die hele verdeel is | |
| Onegte breuk | Gelykwaardige breuke (breuke wat ewe groot is) | |
| Gemengde getal | Teller is groter as noemer en die breuk is altyd groter as 1 |
1. Kom ons hersien nog! Werk saam met ‘n maat en sê watter breukdeel van die vierkant word voorgestel deur:
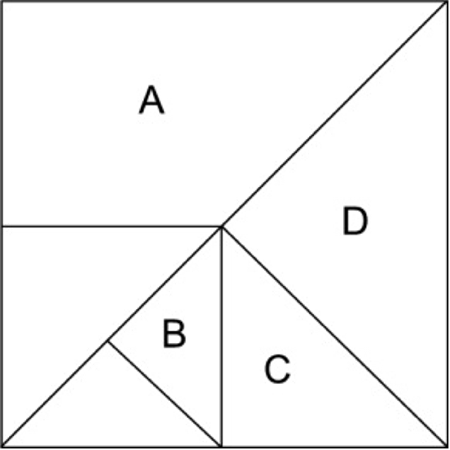
A : ………………………………………………
B : ………………………………………………
C : ………………………………………………
A + C : …………………………………………..
B + C : …………………………………………..
C + D : …………………………………………..
A + D : …………………………………………..
A + B : …………………………………………..
B + D : …………………………………………..
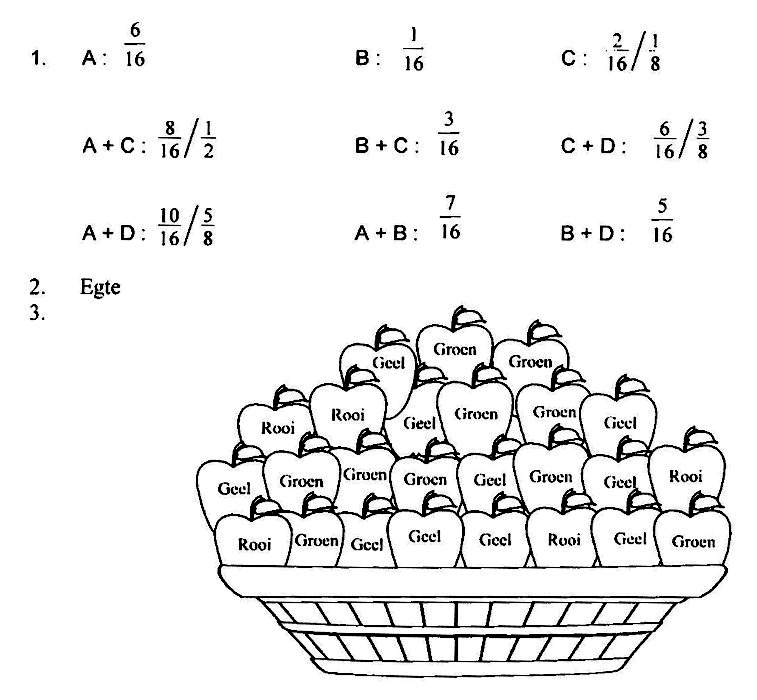
2. Al jul antwoorde is ……………………………………………………. breuke.
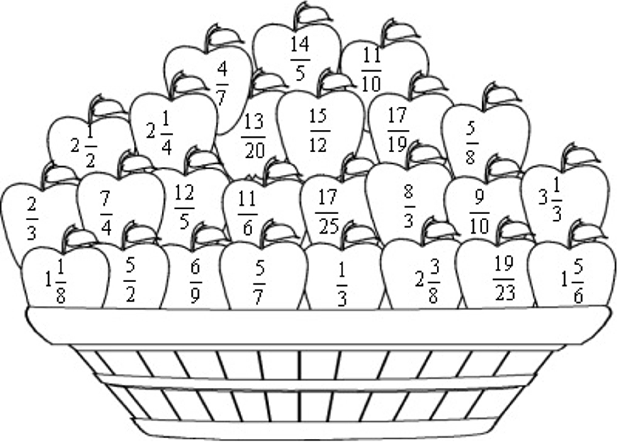
3. Kyk na die bak appels. Kleur die egte breuke appels geel in; die onegtes groen en die gemengde getalle rooi:
Leeruitkomste 1: Die leerder is in staat om getalle en die verwantskappe daarvan te herken, te beskryf en voor te stel, en om tydens probleemoplossing bevoeg en met selfvertroue te tel, te skat, te bereken en te kontroleer.
Assesseringstandaard 1.3: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder die volgende getalle voorstel en herken sodat dit beskryf en vergelyk kan word:
1.3.3 gewone breuke, insluitend spesifiek tiendes, honderdstes en persentasies.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wiskunde graad 6' conversation and receive update notifications?