| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
23.4.2 a) 0,041
23.6 a) 1,234
25. a) R51
Cost per call: R1,77
23.4 DIVISION BY MULTIPLES OF 10
23.4.1 Do you still remember?
a) This is how I divide 0,8 by 40:
0,8 ÷ 40 = (0,8 ÷ 10) ÷ 4
= 0,08 ÷ 4
= 0,02
b) When I divide 4,2 by 600, I say:
4,2 ÷ 600 = (4,2 ÷ 100) ÷ 6
= 0,042 ÷ 6
= 0,007
23.4.2 Calculate the following without a calculator:
a) j = 3,28 ÷ 80
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
b) d = 567 ÷ 700
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
c) g = 18,6 ÷ 2 000
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
23.5 DIVISION WITH DECIMAL FRACTIONS
23.5.1 Work through the following examples with a friend:
A roll of material is 11,25 m long. 1,5 m of material is needed to make one dress.
How many dresses can be cut from this roll of material?
a) I must calculate 11,25 ÷ 1,5
I change the decimal fractions to fractions:
en
I make use of equivalent fractions :
c) I must calculate 11,25 ÷ 1,5I change the divisor to a whole number so that I can divide easier.
1,5 × 10 = 15
To keep the balance in the sum, I must also multiply the dividend by 10!
11,25 × 10 = 112,5
| 7 | ,5 | |||
| 15 | 112 | ,5 | ||
| –105 | ||||
| 7 | 5 | |||
| –7 | 5 | |||
| · | · |
The answer is thus 7,5 dresses..
23.5.2 Which of the above-mentioned methods are precisely the same?
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
23.5.2 Which of the above-mentioned methods are precisely the same?
23.6 Calculate the following by first changing the divisor to a whole number:
a) q = 0,88848 ÷ 0,72
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
b) p = 0,14365 ÷ 0,17
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
c) v = 0,30366 ÷ 0,042
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
24. Time for self-assessment
|
YES | NO | |
| I can divide decimal fractions by 10 correctly. | |||
| I can divide decimal fractions by 100 correctly. | |||
| I can divide decimal fractions by 1 000 correctly. | |||
| I know how to divide decimal fractions by multiples of 10. | |||
| I can divide decimal fractions by decimal fractions. |
25. Look at the following telephone account and answer the questions. You may use your calculator.
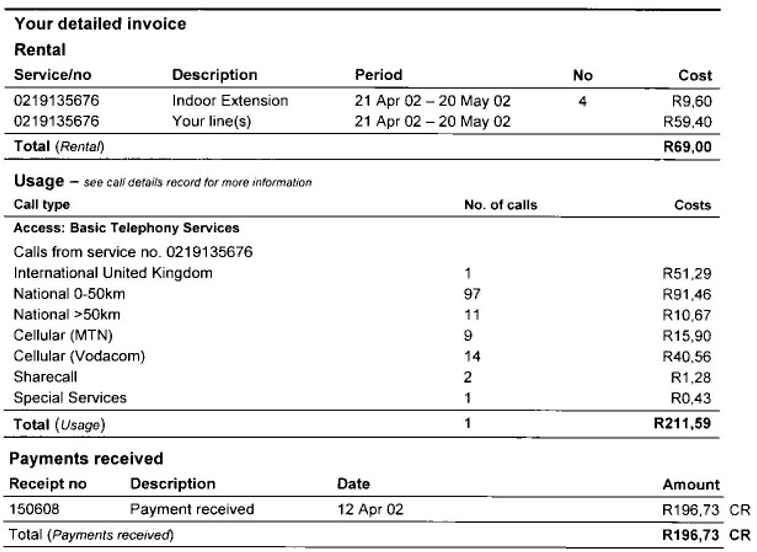
a) Round off the cost of the overseas call to the nearest rand. ……………………
b) What is the total cost of the calls that were made? …………………………….
c) Round off the above answer to the nearest cent. ………………………………
d) What was the average cost of each cell phone (Vodacom) call? ………………
e) Is MTN cheaper than Vodacom? ……………….. Motivate. ………………...
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
f) Round off the cost of the national calls (0 – 50 km) to 1 digit after the comma.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
g) What is the total cost of the national calls? ……………………………………
h) If two “ShareCall” calls cost R1,28, what would 48 such calls cost?
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
i) The account is paid with a R200 note and a R20 note. How much change will be given?
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
j) How much is YOUR telephone account each month, on average, over a period of one year?
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.5: We know this when the learner solves problems in context including contexts that may be used to build awareness of other Learning Areas, as well as human rights, social, economic and environmental issues such as:
1.5.1 financial (including profit and loss, budgets, accounts, loans, simple interest, hire purchase, exchange rates);
Assessment Standard 1.7: We know this when the learner estimates and calculates by selecting and using operations appropriate to solving problems that involve:
1.7.5 division of positive decimals with at least 3 decimal places by whole numbers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?