| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Bài thí nghiệm này trang bị cho sinh viên một số kiến thức cơ bản để xây dựng giao diện người dùng trong môi trường Matlab, nhằm hoàn thiện một chương trình ứng dụng nhất định.
[1].The Mathworks Inc., Matlab Notebook User’s Guide, 2003.
[2].Nguyễn Hữu Tình - Lê Tấn Hùng - Phạm Thị Ngọc Yến - Nguyễn Thị Lan Hương, Cơ sở Matlab&ứng dụng, NXB KH và Kỹ thuật, 1999.
[3].Nguyễn Hoài Sơn - Đỗ Thanh Việt - Bùi Xuân Lâm, Ứng dụng MATLAB trong tính toán kỹ thuật, Tập 1, NXB ĐHQG Tp. HCM, 2000 (trang 328-344).
Cũng như các ngôn ngữ cấp cao khác, Matlab hổ trợ nhiều công cụ chức năng cho phép lập trình tạo giao diện sử dụng đẹp và nhanh chóng. Ví dụ, các dạng nút ấn, cửa sổ soạn thảo, các dạng menu, … như hình 6.1.
***SORRY, THIS MEDIA TYPE IS NOT SUPPORTED.***
Hình 6.1 – Các công cụ hổ trợ giao diện
Trong bài thí nghiệm này, sinh viên lần lượt thực hiện các bước được nêu ra để được một giao diện đơn giản như hình vẽ 6.2. Trong mỗi bước thực hành, sinh viên hãy quan sát kỹ đáp ứng của chương trình, từ đó tự mình rút ra kinh nghiệm về việc điều chỉnh các thuộc tính đồ hoạ của Matlab.
Tạo cửa sổ chính figure – ‘Welcome to User Interface’s Giude’ theo cách sau:
% User Interface's Guide
%
% Matlab Experiments 2003
% TcAD, CIT, Cantho University
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Initialize whole figure...
namefig = 'Welcome to User Interface''s Guide';
figpos = get(0,'DefaultFigurePosition'); % lay vi tri mac nhien
figpos(1)= figpos(1)-10; figpos(2)= figpos(2)-10;
figpos(3)= figpos(3)+10; figpos(4)= figpos(4)+10;
% Tao figure
fig=figure( ...
'Name', namefig, ...
'NumberTitle','off', ...
'Position',figpos);
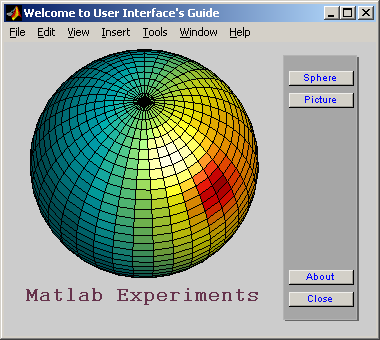
Hình 6.2 – Một giao diện đơn giản
Quan sát kết quả trên hình 6.3 (Lưu ý các thuộc tính: Name, Position)
(Hình 6.3)
Thêm vào figure một axes cho phép hiển thị đồ họa:
% --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% main axes
axs=axes('Position',[0.05 0.4 0.65 0.55]);
(Hình 6.4)
Hiển thị dòng ‘Matlab Experiments’ bên dưới axes:
% --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% text
txtpos=[10 50 425 50];
txt=uicontrol(...
'Style','text',...
'BackgroundColor',[0.8 0.8 0.8],...
'ForegroundColor',[0.4 0.5 0.3],...
'String','Matlab Experiments',...
'Position',txtpos,...
'Fontname','Courier',...
'FontWeight','Bold',...
'FontSize',26);
(Hình 6.5)
Tạo một frame có shadow bên phải figure để đặt các nút chức năng:
% --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Console frames
p1=0.755; p2=0.05; p3=0.2; p4=0.90;
frm1pos = [p1 p2 p3 p4];
frm2pos = [p1-0.005 p2+0.005 p3 p4];
% shadow frame
frm1=uicontrol( ...
'Style','frame', ...
'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',frm1pos, ...
'ForegroundColor',[0.4 0.4 0.4],...
'BackgroundColor',[0.4 0.4 0.4]);
% main frame
frm2=uicontrol( ...
'Style','frame', ...
'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',frm2pos, ...
'ForegroundColor',[0.7 0.7 0.7],...
'BackgroundColor',[0.65 0.65 0.65]);
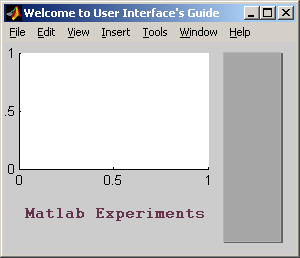
(Hình 6.6)
Tạo nút ‘Close’ có chức năng đóng cửa sổ figure hiện hành:
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Close button
closeHndl=uicontrol(...
'Style','pushbutton', ...
'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[p1+0.01 p2+0.05 p3-0.025 0.05], ...
'String','Close', ...
'Foregroundcolor','b',...
'Fontsize',9,...
'Callback','close');
Vấn đề quan trọng nhất đối với một nút chức năng là thi hành công việc tương ứng khi người sử dụng thao tác. Thuộc tính ‘CallBack’ cho phép: thi hành một lệnh của Matlab dưới dạng chuỗi (bao gồm lệnh gọi hàm, script file, biểu thức toán, …). Sinh viên thử thay lệnh close bằng một lệnh khác, chẳng hạn demos và quan sát đáp ứng.
Tạo nút Sphere để vẽ một hình cầu 3D:
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Sphere button
sph=uicontrol( ...
'Style','pushbutton', ...
'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[p1+0.01 p4-0.05 p3-0.025 0.05], ...
'String','Sphere', ...
'Foregroundcolor','b',...
'Fontsize',9,...
'Callback',['[x,y,z]=sphere(35);', 'surfl(x,y,z);', 'axis equal']);
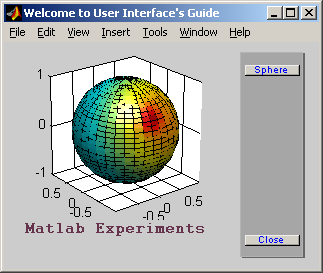
(Hình 6.7)
Tạo nút Picture để hiển thị ảnh màu:
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Picture button
pic=uicontrol( ...
'Style','pushbutton', ...
'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[p1+0.01 p4-0.125 p3-0.025 0.05], ...
'String','Picture', ...
'Foregroundcolor','b',...
'Fontsize',9,...
'Callback',['imshow(imread(''flowers.tif''))']);
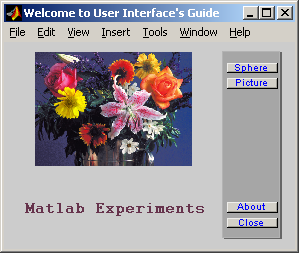
(Hình 6.8)
Sinh viên lưu ý cách biểu diễn nhiều lệnh ở dạng chuỗi cho ‘CallBack’. Trong trường hợp có quá nhiều lệnh phục vụ chức năng này, ta nên đưa chúng vào một script file hoặc một hàm khác. Ngoài ra, nếu ta tạo giao diện dưới dạng một hàm (function) thì thuộc tính ‘CallBack’ cho phép gọi một hàm con được viết ngay trong file này.
Sinh viên hãy tạo thêm nút ‘About’ sao cho khi người sử dụng ấn nút sẽ mở cửa sổ mới nằm ngay giữa màn hình 6.9.
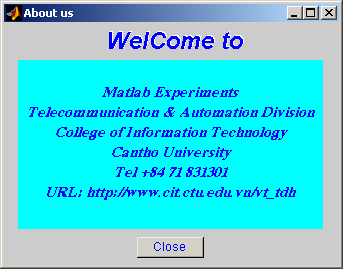
(Hình 6.9)
Sinh viên hãy xem một số file tạo giao diện demo của các toolbox trong Matlab chẳng hạn: graf3d.m trong \toolbox\matlab\demos, để tham khảo cách xây dựng giao diện theo dạng hàm. Với cách này, thuộc tính ‘CallBack’ trong ‘uicontrol’ cho phép gọi trực tiếp một hàm mà hàm đó được xây dựng ngay trong file giao diện (nghĩa là không cần tạo một file *.m khác phục vụ cho ‘CallBack’).
Thử sửa lại giao diện của bài thí nghiệm này theo dạng trên.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Thí nghiệm cad (computer-aided design)' conversation and receive update notifications?