| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
After reading this module, students should be able to
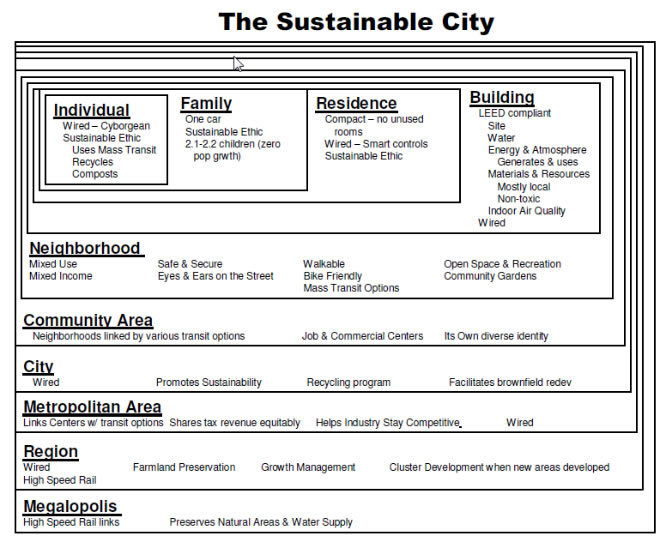
Sustainability, from science to philosophy to lifestyle, finds expression in the way we shape our cities. Cities are not just a collection of structures, but rather groups of people living different lifestyles together. When we ask if a lifestyle is sustainable, we’re asking if it can endure. Some archaeologists posit that environmental imbalance doomed many failed ancient civilizations.
Montgomery, David,
Dirt, The Erosion of Civilizations, University of California Press, 2007
Throughout history settlement patterns have been set by technology and commerce. Civilizations have produced food, clothing and shelter, and accessed foreign markets to purchase and sell goods. Workers traditionally had to live near their place of occupation, although in modern industrial times advanced transportation systems have enabled us to live quite a distance from where we work.
In hindsight we can see how reliance on water and horse-drawn transportation shaped historical civilizations and how this equation was radically altered with the rise of the automobile following World War II. While attempting to envision the “Sustainable City” we must discern what factors will influence its shape and form in the future.
For the last century energy has been affordable and plentiful, limited mainly by our technological ability to use it. Contemporary civilization consumes 474 exajoules (474×10
18 J=132,000 TWh). This is equivalent to an average annual power consumption rate of 15 terawatts (1.504×10
13 W).
Energy - Consumption'!A1 "Consumption by fuel, 1965 - 2008" (XLS).
Statistical Review of World Energy 2009 ,
BP . July 31, 2006. Retrieved 2009-10-24. Hawken, Paul;
The Ecology of Commerce, a Declaration of Sustainability ; Harper Buisness, 1993, p.76

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?