| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This is the most common way of grouping living things based on simple distinctive characteristics. Classification systems are always changing as newinformation is made available. Modern technologies such as electron microscopy make it possible to observe microscopic organisms in greater detail. Thecurrent system was developed by Robert H. Whittaker in 1969 and was built on the work of previous biologists such as Carolus Linnaeus. The highest groupingis called a kingdom .
Five kingdoms: http://www.tutorvista.com/content/biology/biology-iii/modern-classification /five-kingdom-classification.php
Bug scope: Images of microscopic organisms http://bugscope.beckman.uiuc.edu/
Neok12: Animals and wildlife videos http://www.neok12.com/Animals-Wildlife.htm
Encyclopedia of life: Images and explanations of terms http://eol.org/index
Living things can be classified into five major kingdoms:
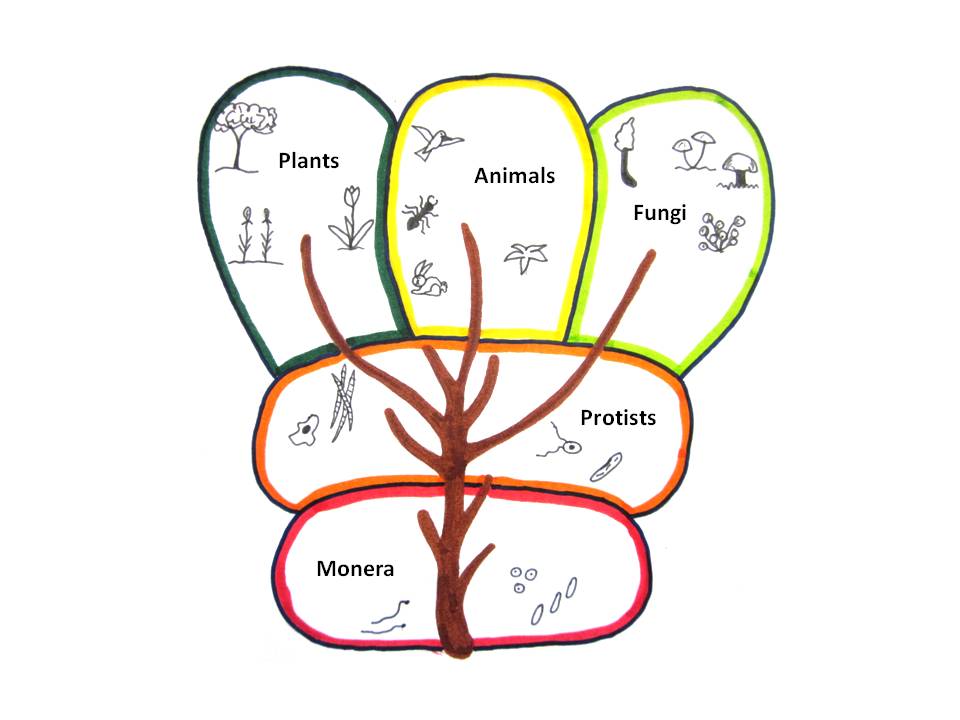
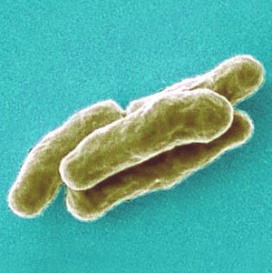
Kingdom Monera (Bacteria)
Kingdom Protista
Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Plantae
Kingdom Animalia
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5uJ8QeFRvJA&feature=related A video showing a brief summary of the five kingdoms
chloroplasts, Golgi complex, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
Interesting fact: Bacteria are found everywhere and are the most numerous organisms on Earth. In a single gram of soil, there are about 40 millionbacterial cells. The human body also contains 10 times as many bacterial cells as human cells!!
http://blog.ted.com/2008/05/06/paul_stamets/ A TED video on the many uses of Fungi
Additional resource:
Projects and assignments:
1. Research one beneficial and one harmful application of one member from each kingdom, with examples from their use in South Africa. Students can be groupedinto smaller groups and each one is given one kingdom to research. (Use www.arkive.org as a research tool for your favourite animal or plant or http://bugscope.becnkman.uiuc.edu/ for nice pictures of insects). Results can be presented in the form of a poster.
2. Go to your nearest supermarket or garden and find one representative organism for each kingdom. Present this information by drawing diagrams.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula: life sciences grade 10' conversation and receive update notifications?